Publications
✉️ represents corresponding author.
2023
-
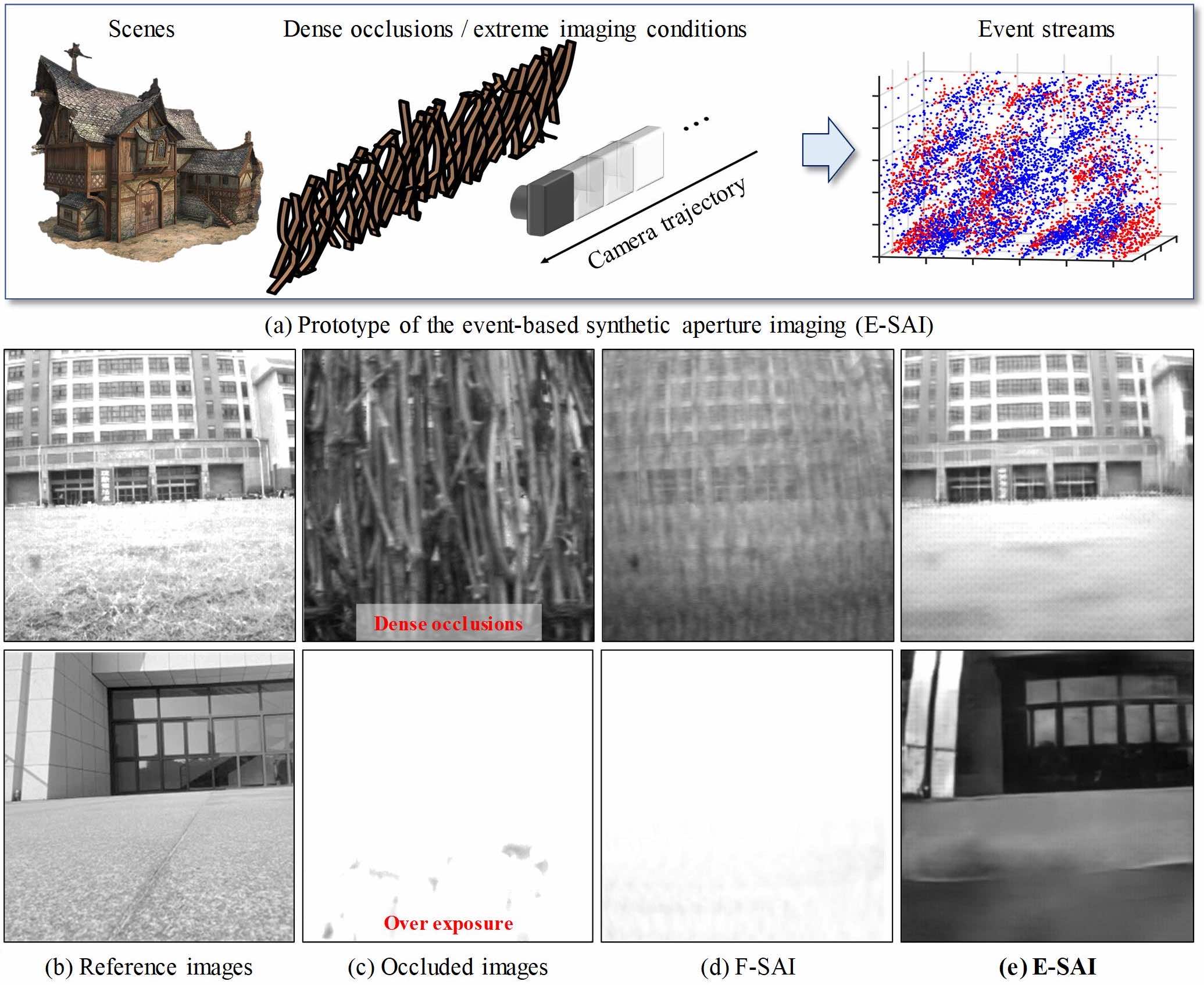 Learning to See Through with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Zhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal!
Learning to See Through with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Zhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal!@article{yu2022, title = {Learning to See Through with Events}, author = {Yu, Lei and Zhang, Xiang and Liao, Wei and Yang, Wen and Xia, Gui-Song}, year = {2023}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}, dataset = {https://drive.google.com/file/d/19SnoRfVgvKlUspAyzbBhtXszXkh5NsbS/view?usp=sharing} } -
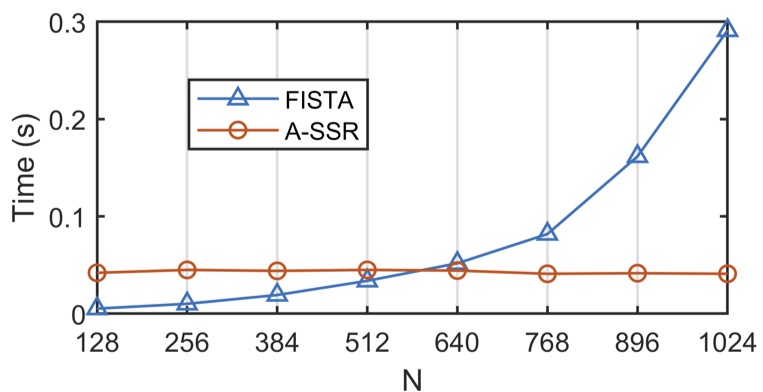 Spiking Sparse Recovery with Non-convex PenaltiesZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Eldar YoninaIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023
Spiking Sparse Recovery with Non-convex PenaltiesZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Eldar YoninaIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023@article{yu2022a, title = {Spiking Sparse Recovery with Non-convex Penalties}, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei and Zheng, Gang and Eldar, Yonina}, year = {2023}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing} } -
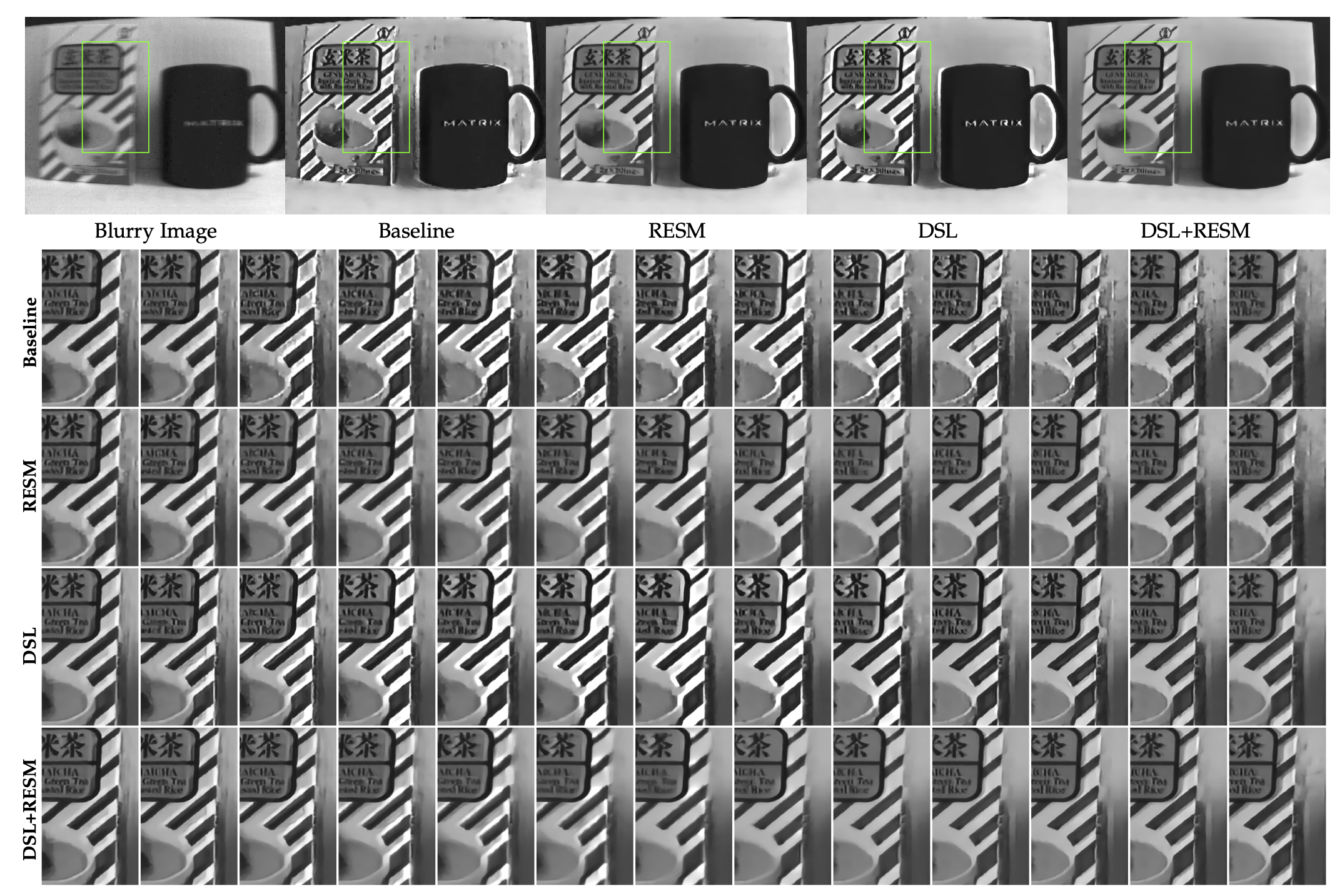 Learning to Super-Resolve Blurry Images with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Zhang Xiang, Zhang Haijian, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia GuisongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal
Learning to Super-Resolve Blurry Images with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Zhang Xiang, Zhang Haijian, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia GuisongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal@article{yu2022b, author = {Yu, Lei and Wang, Bishan and Zhang, Xiang and Zhang, Haijian and Yang, Wen and Liu, Jianzhuang and Xia, Guisong}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}, number = {0}, title = {Learning to Super-Resolve Blurry Images with Events}, volume = {0}, year = {2023} } -
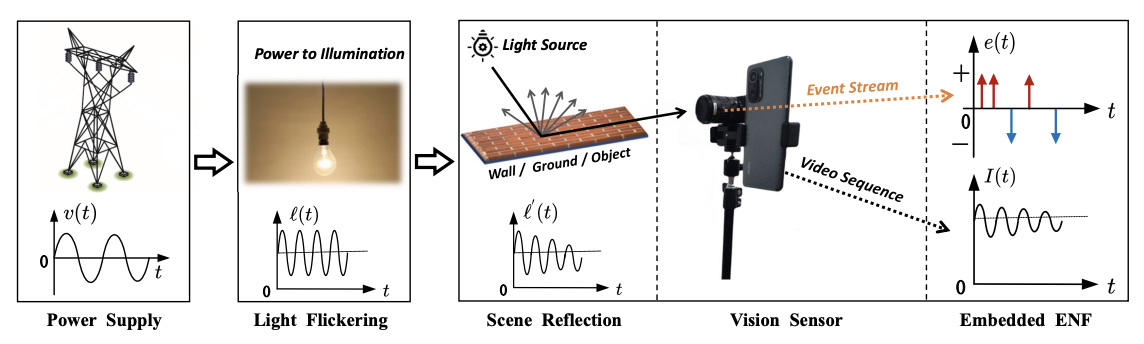 "Seeing" Electric Network Frequency From EventsXu Lexuan, Hua Guang, Zhang Haijian, Yu Lei ✉️, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2023🔥 First work on event-based ENF estimation!
"Seeing" Electric Network Frequency From EventsXu Lexuan, Hua Guang, Zhang Haijian, Yu Lei ✉️, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2023🔥 First work on event-based ENF estimation!@inproceedings{xu2023seeing, title = {"Seeing" Electric Network Frequency From Events}, author = {Xu, Lexuan and Hua, Guang and Zhang, Haijian and Yu, Lei and Qiao, Ning}, booktitle = {CVPR}, pages = {18022--18031}, year = {2023} } -
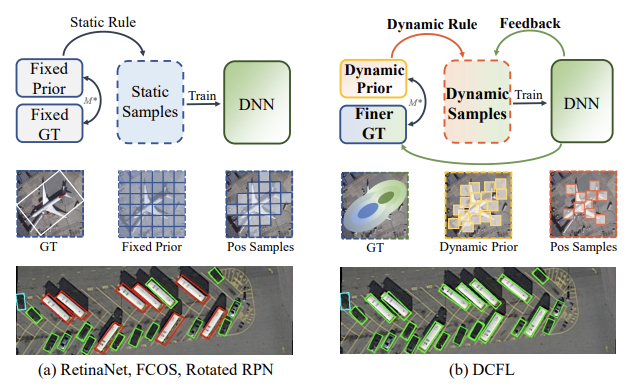 Dynamic Coarse-To-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Ding Jian, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei ✉️, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2023
Dynamic Coarse-To-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Ding Jian, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei ✉️, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2023@inproceedings{Xu_2023_CVPR, author = {Xu, Chang and Ding, Jian and Wang, Jinwang and Yang, Wen and Yu, Huai and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song}, title = {Dynamic Coarse-To-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object Detection}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2023}, pages = {7318-7328} } -
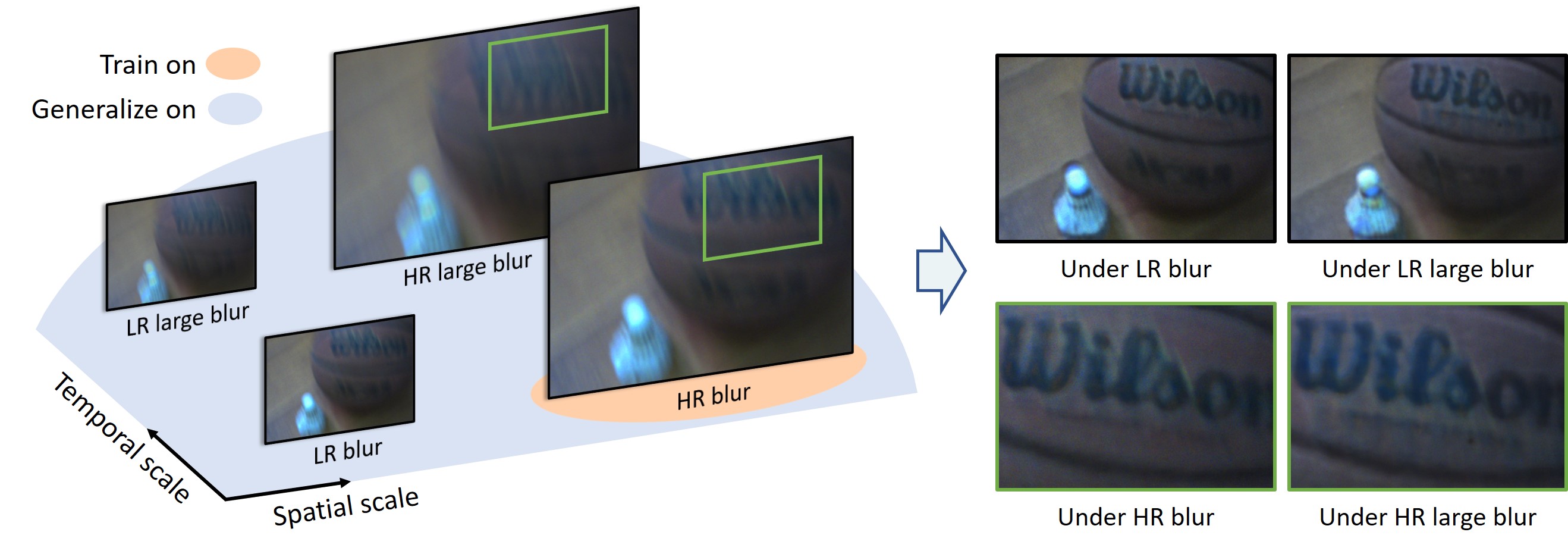 Generalizing Event-Based Motion Deblurring in Real-World ScenariosZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia Gui-SongIn ICCV, 2023
Generalizing Event-Based Motion Deblurring in Real-World ScenariosZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia Gui-SongIn ICCV, 2023@inproceedings{Zhang2023, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Liu, Jianzhuang and Xia, Gui-Song}, booktitle = {ICCV}, title = {Generalizing Event-Based Motion Deblurring in Real-World Scenarios}, year = {2023} }
2022
-
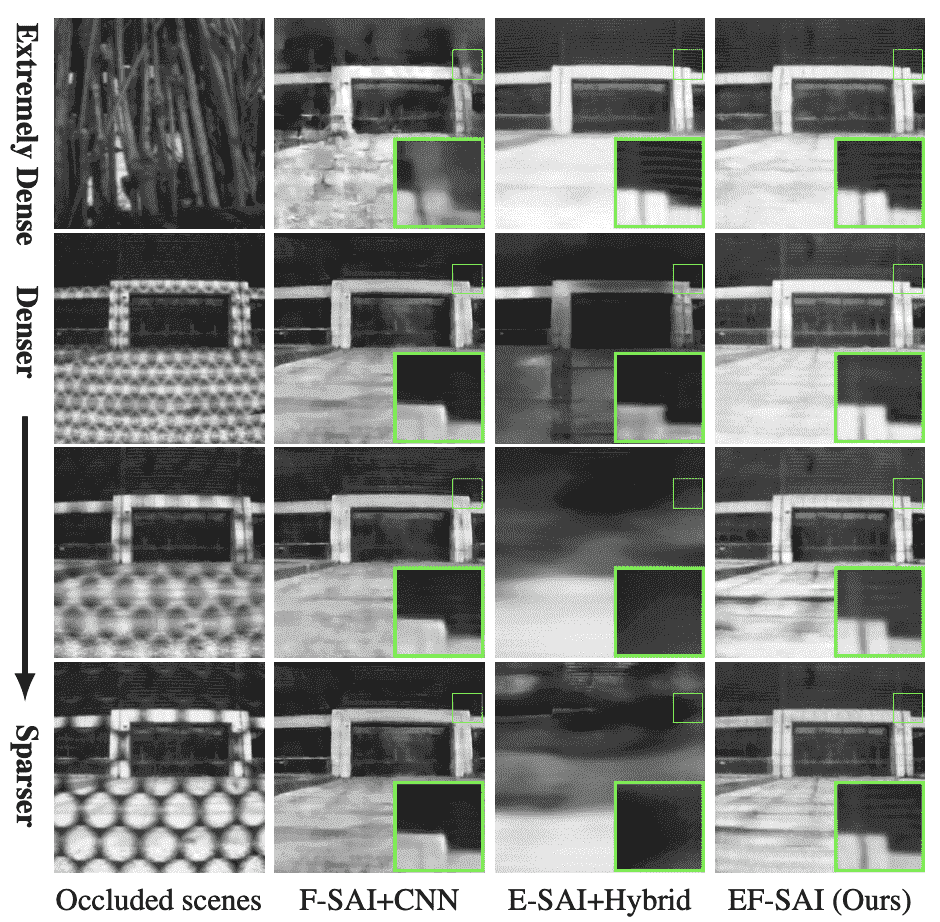 Synthetic aperture imaging with events and framesLiao Wei, Zhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2022🔥 A new SAI method by fusing events and frames.
Synthetic aperture imaging with events and framesLiao Wei, Zhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2022🔥 A new SAI method by fusing events and frames.@inproceedings{Liao2022, title = {Synthetic aperture imaging with events and frames}, author = {Liao, Wei and Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei and Lin, Shijie and Yang, Wen and Qiao, Ning}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2022} } -
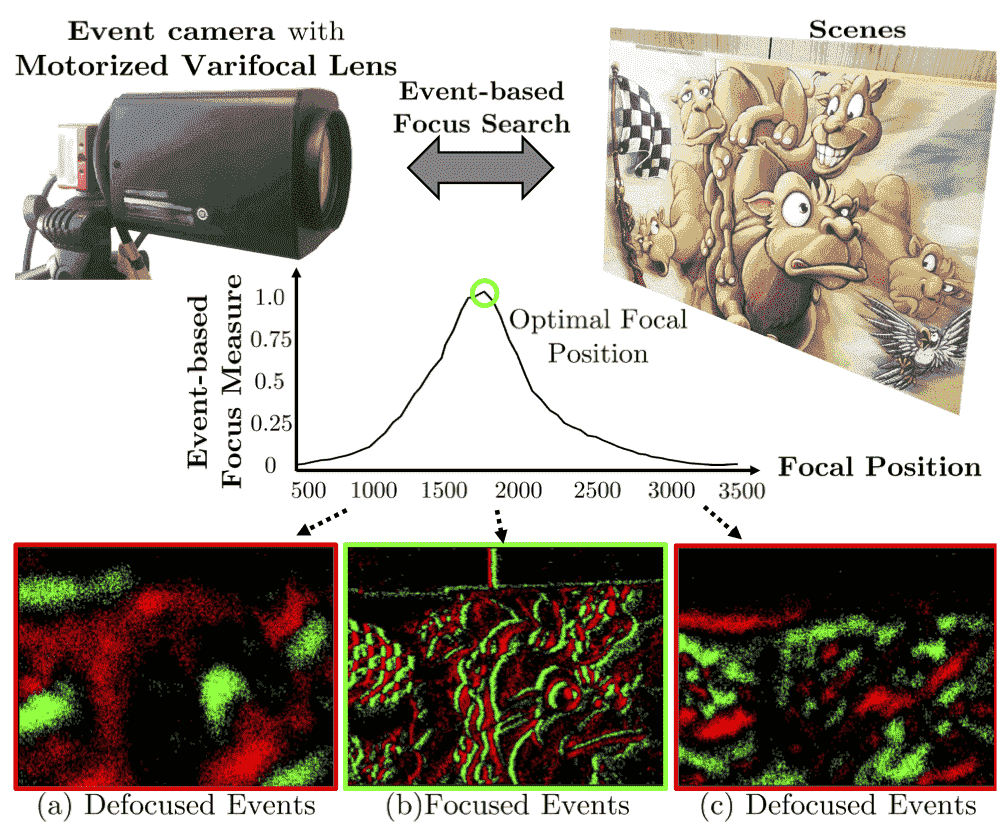 Autofocus for event camerasLin Shijie, Zhang Y, Yu Lei, Zhou B., Luo X., and Pan JianIn CVPR, 2022🔥 Oral paper
Autofocus for event camerasLin Shijie, Zhang Y, Yu Lei, Zhou B., Luo X., and Pan JianIn CVPR, 2022🔥 Oral paper@inproceedings{Lin2022, title = {Autofocus for event cameras}, author = {Lin, Shijie and Zhang, Y and Yu, Lei and Zhou, B. and Luo, X. and Pan, Jian}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2022} } -
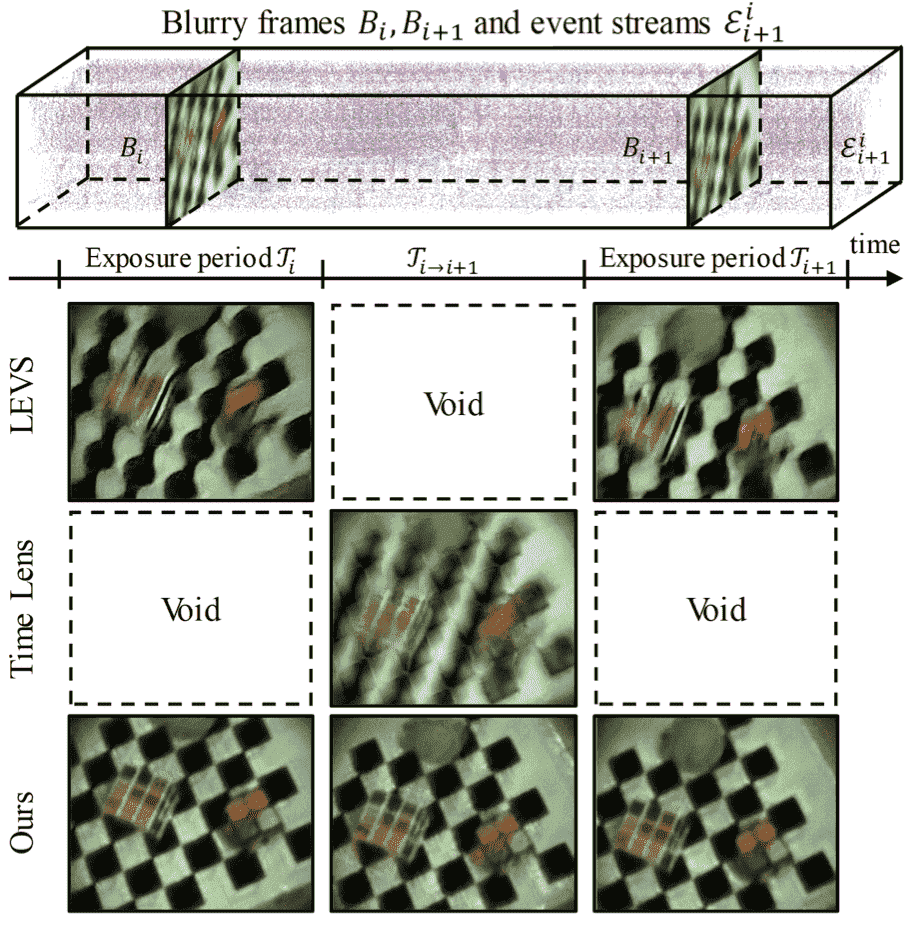 Unifying motion deblurring and frame interpolation with eventsZhang Xiang, and Yu Lei ✉️In CVPR, 2022🔥 Self-supervised EVDI
Unifying motion deblurring and frame interpolation with eventsZhang Xiang, and Yu Lei ✉️In CVPR, 2022🔥 Self-supervised EVDI@inproceedings{Zhang2022, title = {Unifying motion deblurring and frame interpolation with events}, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2022} } -
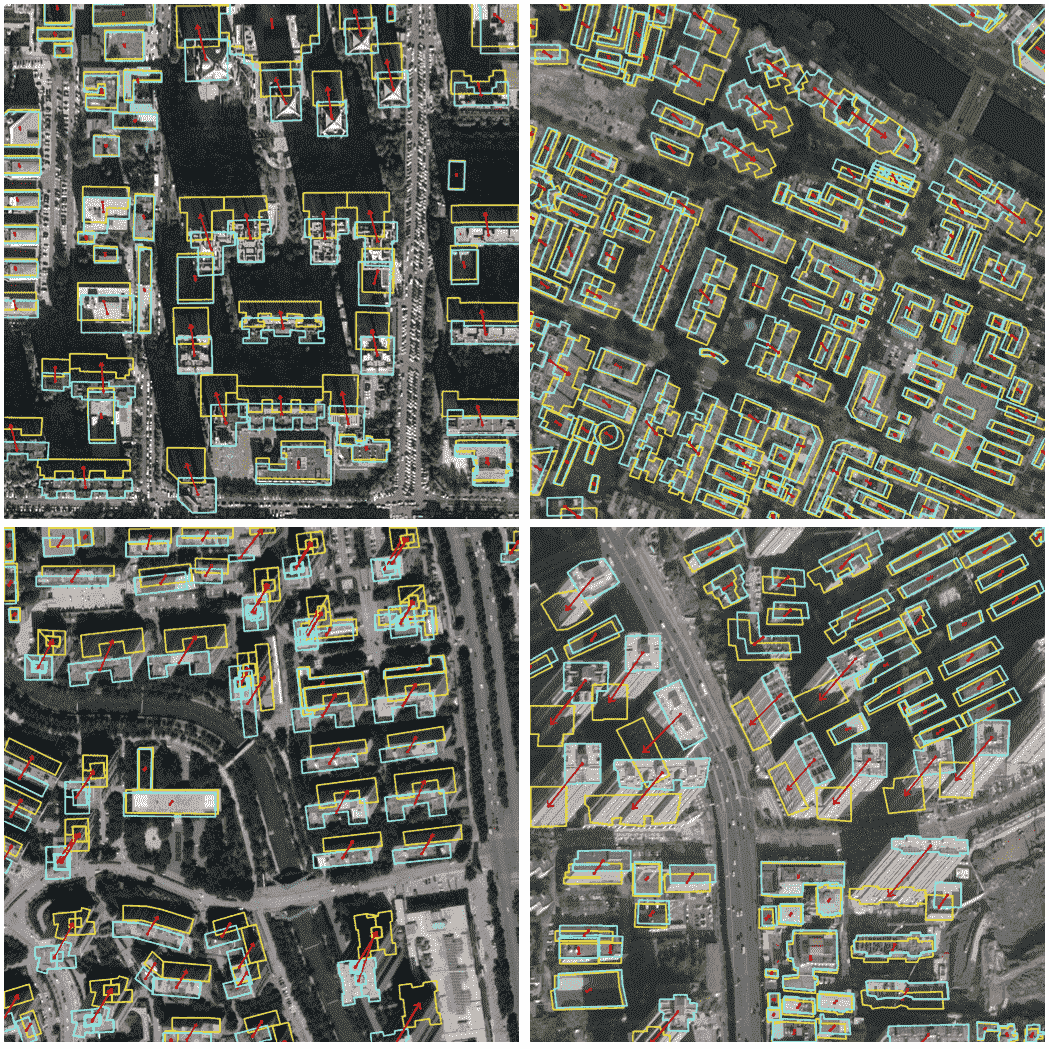 Learning to Extract Building Footprints from Off-Nadir Aerial ImagesWang Jinwang, Meng L., Li W., Yang Wen, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2022🔥 Top Journal
Learning to Extract Building Footprints from Off-Nadir Aerial ImagesWang Jinwang, Meng L., Li W., Yang Wen, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2022🔥 Top Journal@article{wang2022, title = {Learning to Extract Building Footprints from Off-Nadir Aerial Images}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}, author = {Wang, Jinwang and Meng, L. and Li, W. and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song}, year = {2022} } -
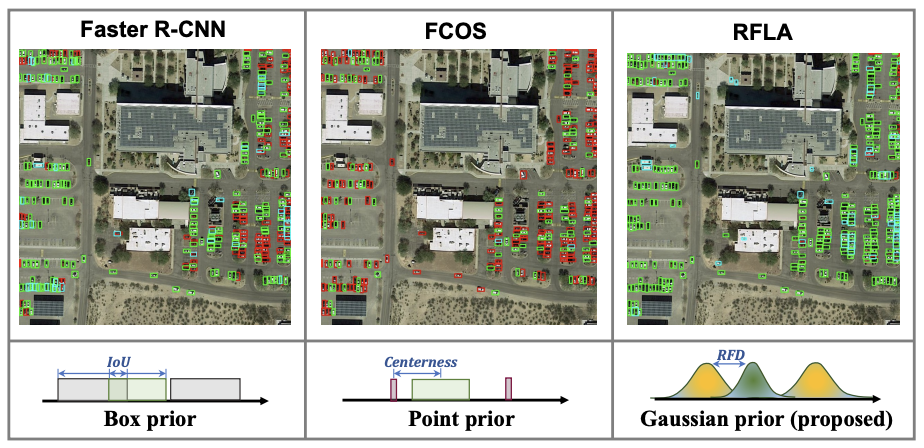 RFLA: Gaussian Receptive Field Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIn European Conference on Computer Vision, 2022
RFLA: Gaussian Receptive Field Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIn European Conference on Computer Vision, 2022@inproceedings{xu2022rfla, title = {RFLA: Gaussian Receptive Field Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object Detection}, author = {Xu, Chang and Wang, Jinwang and Yang, Wen and Yu, Huai and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song}, booktitle = {European Conference on Computer Vision}, pages = {526--543}, year = {2022}, organization = {Springer} }
2021
-
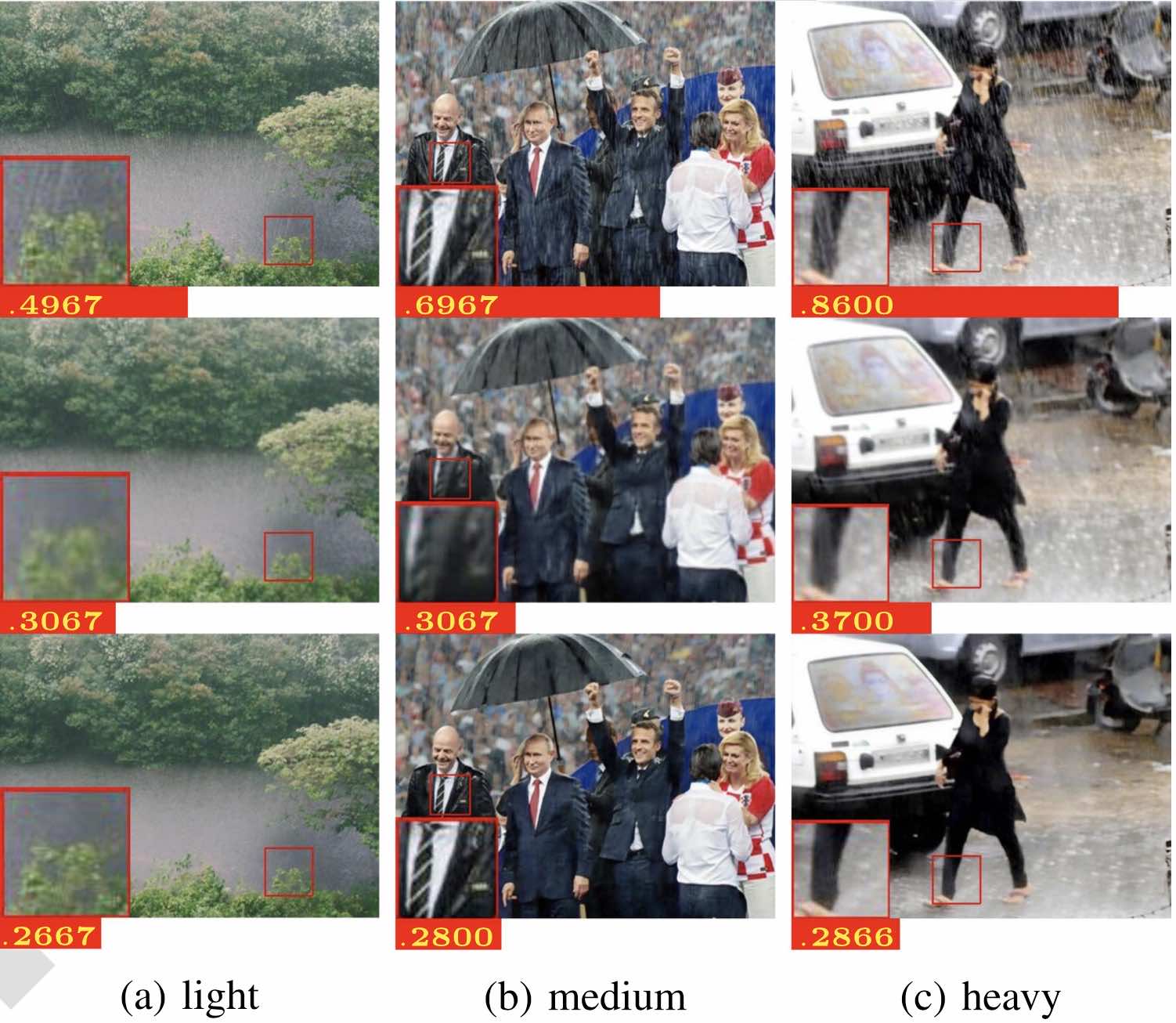 Single Image Deraining With Continuous Rain Density EstimationYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, He Jingwei, Xia Guisong, and Yang WenIEEE Transaction on Multimedia, 2021🔥 A new deraining method considering rain densities.
Single Image Deraining With Continuous Rain Density EstimationYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, He Jingwei, Xia Guisong, and Yang WenIEEE Transaction on Multimedia, 2021🔥 A new deraining method considering rain densities.@article{key, author = {Yu, Lei and Wang, Bishan and He, Jingwei and Xia, Guisong and Yang, Wen}, journal = {IEEE Transaction on Multimedia}, number = {0}, title = {Single Image Deraining With Continuous Rain Density Estimation}, volume = {0}, year = {2021} } -
 Event-based Synthetic Aperture Imaging with a Hybrid NetworkZhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2021🔥 Oral, Best Paper Candidate
Event-based Synthetic Aperture Imaging with a Hybrid NetworkZhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2021🔥 Oral, Best Paper Candidate@inproceedings{zhang2021, title = {Event-based {Synthetic} {Aperture} {Imaging} with a {Hybrid} {Network}}, booktitle = {CVPR}, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Liao, Wei and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Xia, Gui-Song}, year = {2021}, pages = {14235--14244} } -
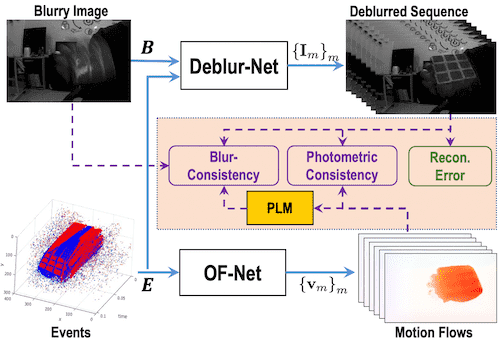 Motion Deblurring with Real EventsXu Fang, Yu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Yang Wen, Xia Guisong, Jia Xu, Qiao Zhendong, and Liu JianzhuangIn ICCV, 2021🔥 A new framework to learn deblurring with real-world events
Motion Deblurring with Real EventsXu Fang, Yu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Yang Wen, Xia Guisong, Jia Xu, Qiao Zhendong, and Liu JianzhuangIn ICCV, 2021🔥 A new framework to learn deblurring with real-world events@inproceedings{xu2021, author = {Xu, Fang and Yu, Lei and Wang, Bishan and Yang, Wen and Xia, Guisong and Jia, Xu and Qiao, Zhendong and Liu, Jianzhuang}, title = {Motion Deblurring with Real Events}, booktitle = {ICCV}, year = {2021} } -
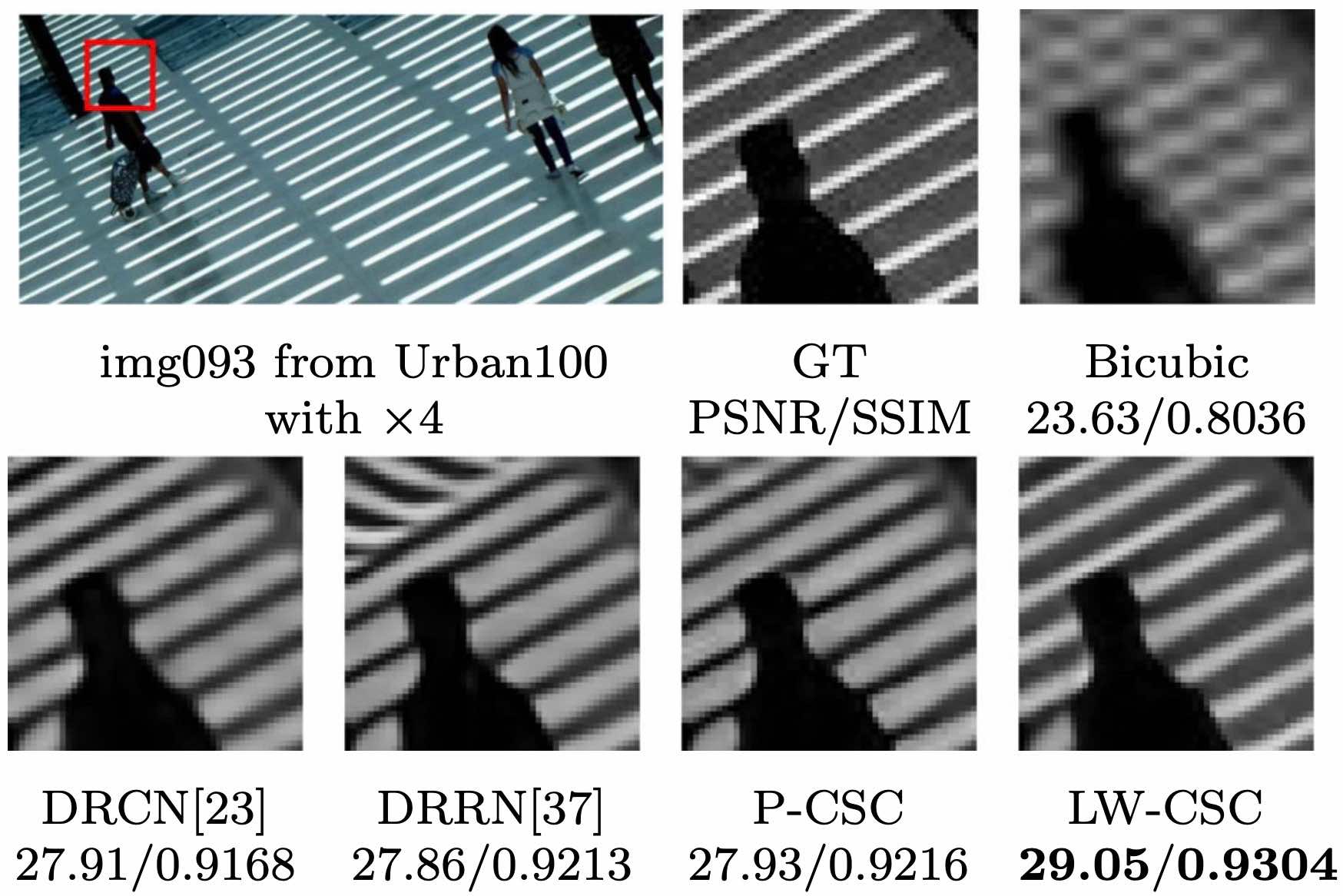 Image super-resolution by learning weighted convolutional sparse codingHe Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Liu Zhou, and Yang WenSignal, Image and Video Processing, 2021
Image super-resolution by learning weighted convolutional sparse codingHe Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Liu Zhou, and Yang WenSignal, Image and Video Processing, 2021@article{he2021, title = {Image super-resolution by learning weighted convolutional sparse coding}, journal = {Signal, Image and Video Processing}, author = {He, Jingwei and Yu, Lei and Liu, Zhou and Yang, Wen}, year = {2021}, pages = {1--9} } -
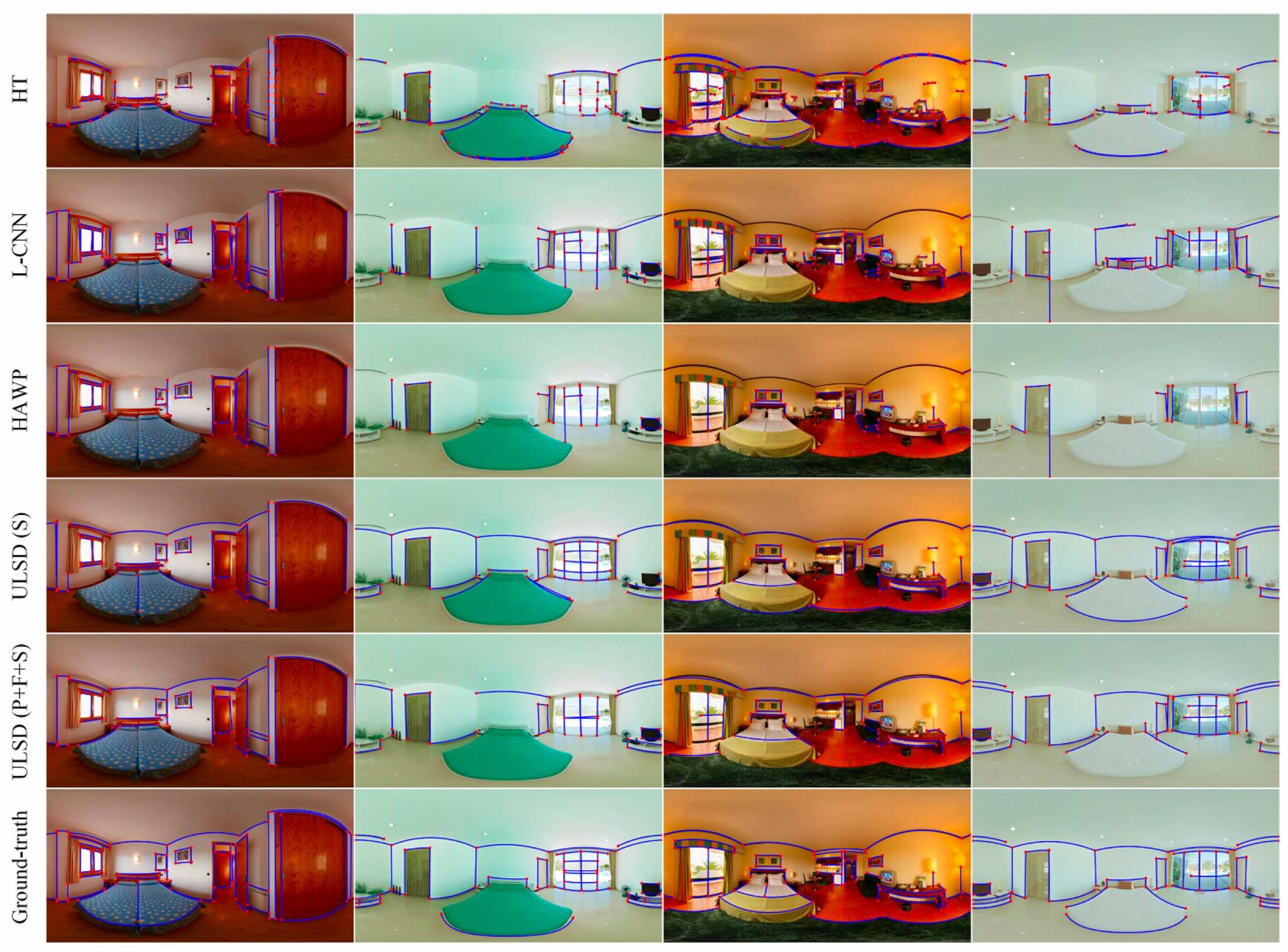 ULSD: Unified line segment detection across pinhole, fisheye, and spherical camerasLi Hao, Yu Huai, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Lei ✉️, and Scherer SebastianISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021🔥 Best Paper of 2021 in ISPRS
ULSD: Unified line segment detection across pinhole, fisheye, and spherical camerasLi Hao, Yu Huai, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Lei ✉️, and Scherer SebastianISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021🔥 Best Paper of 2021 in ISPRS@article{li2021, title = {{ULSD}: {Unified} line segment detection across pinhole, fisheye, and spherical cameras}, volume = {178}, journal = {ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing}, author = {Li, Hao and Yu, Huai and Wang, Jinwang and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Scherer, Sebastian}, year = {2021}, pages = {187--202} }
2020
-
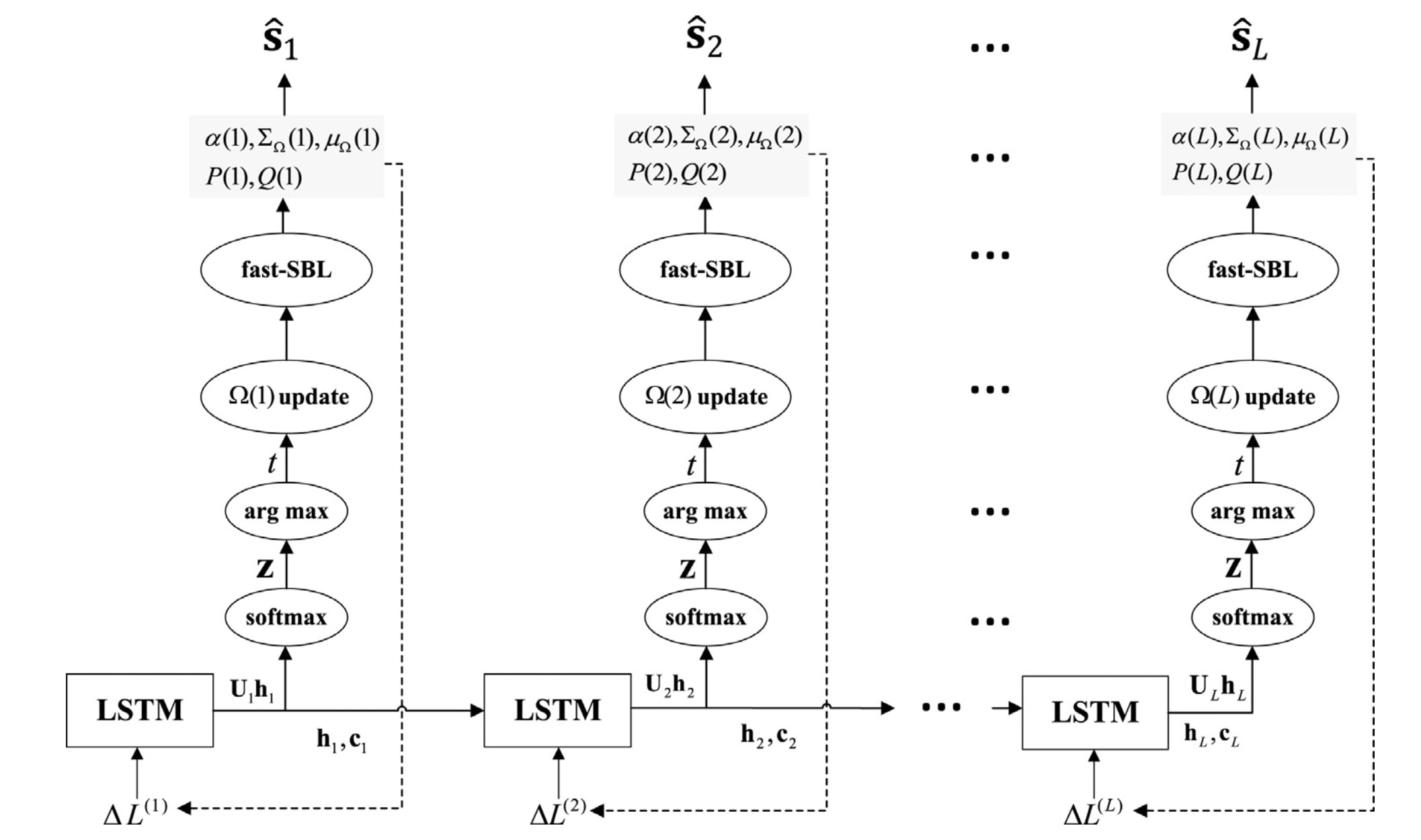 Distributed compressive sensing via LSTM-Aided sparse Bayesian learningZhang Haijian, Zhang Wusheng, Yu Lei ✉️, and Bi GuoanSignal Processing, 2020
Distributed compressive sensing via LSTM-Aided sparse Bayesian learningZhang Haijian, Zhang Wusheng, Yu Lei ✉️, and Bi GuoanSignal Processing, 2020@article{zhang2020f, title = {Distributed compressive sensing via {LSTM}-{Aided} sparse {Bayesian} learning}, volume = {176}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Zhang, Haijian and Zhang, Wusheng and Yu, Lei and Bi, Guoan}, year = {2020}, pages = {107656} } -
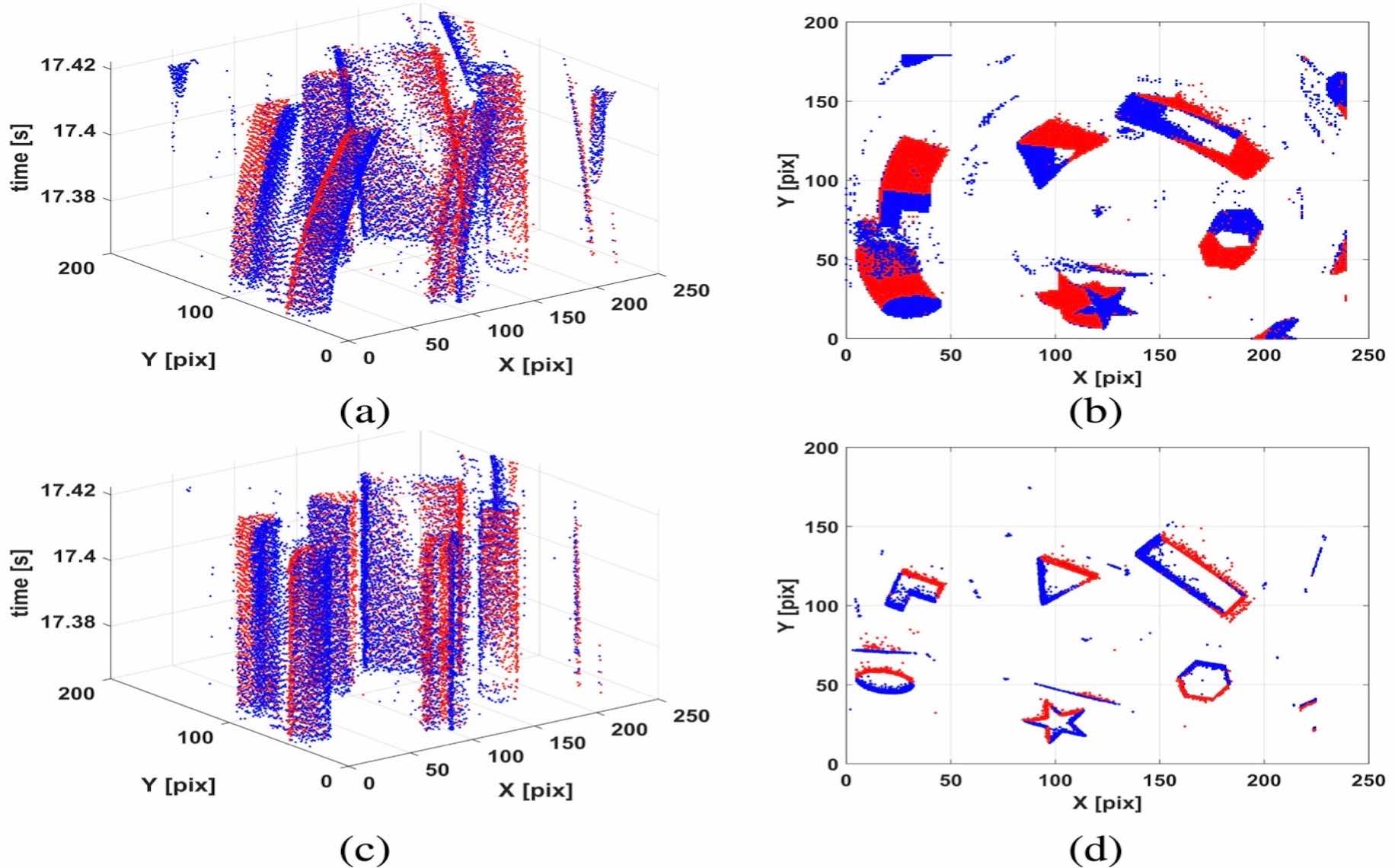 Robust motion compensation for event cameras with smooth constraintXu Jie, Jiang Meng, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Wang WenweiIEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020
Robust motion compensation for event cameras with smooth constraintXu Jie, Jiang Meng, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Wang WenweiIEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020@article{xu2020a, title = {Robust motion compensation for event cameras with smooth constraint}, volume = {6}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging}, author = {Xu, Jie and Jiang, Meng and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Wang, Wenwei}, year = {2020}, pages = {604--614} } -
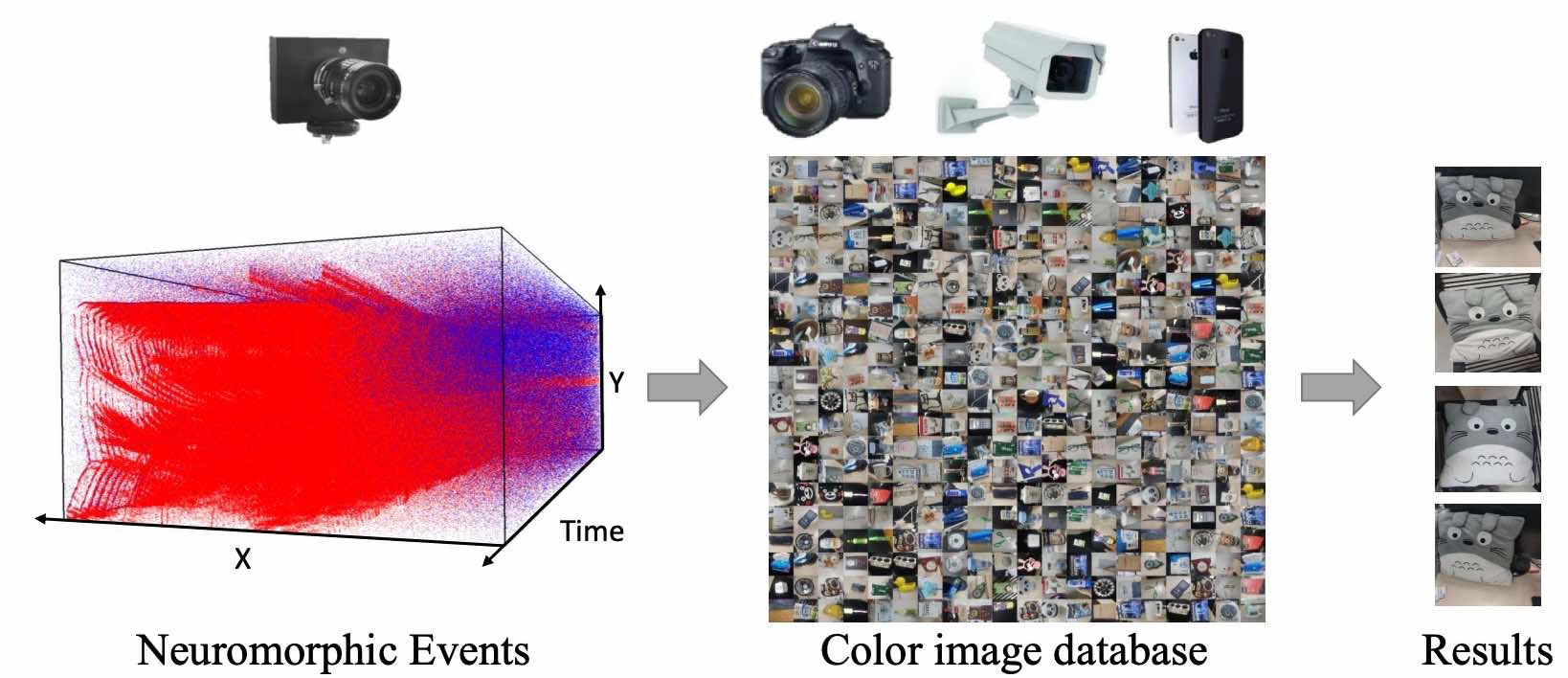 Matching Neuromorphic Events and Color Images via Adversarial LearningXu Fang, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Dai Dengxin, and Xia Gui-songarXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00636, 2020
Matching Neuromorphic Events and Color Images via Adversarial LearningXu Fang, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Dai Dengxin, and Xia Gui-songarXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00636, 2020@article{xu2020matching, title = {Matching Neuromorphic Events and Color Images via Adversarial Learning}, author = {Xu, Fang and Lin, Shijie and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Dai, Dengxin and Xia, Gui-song}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00636}, year = {2020} } -
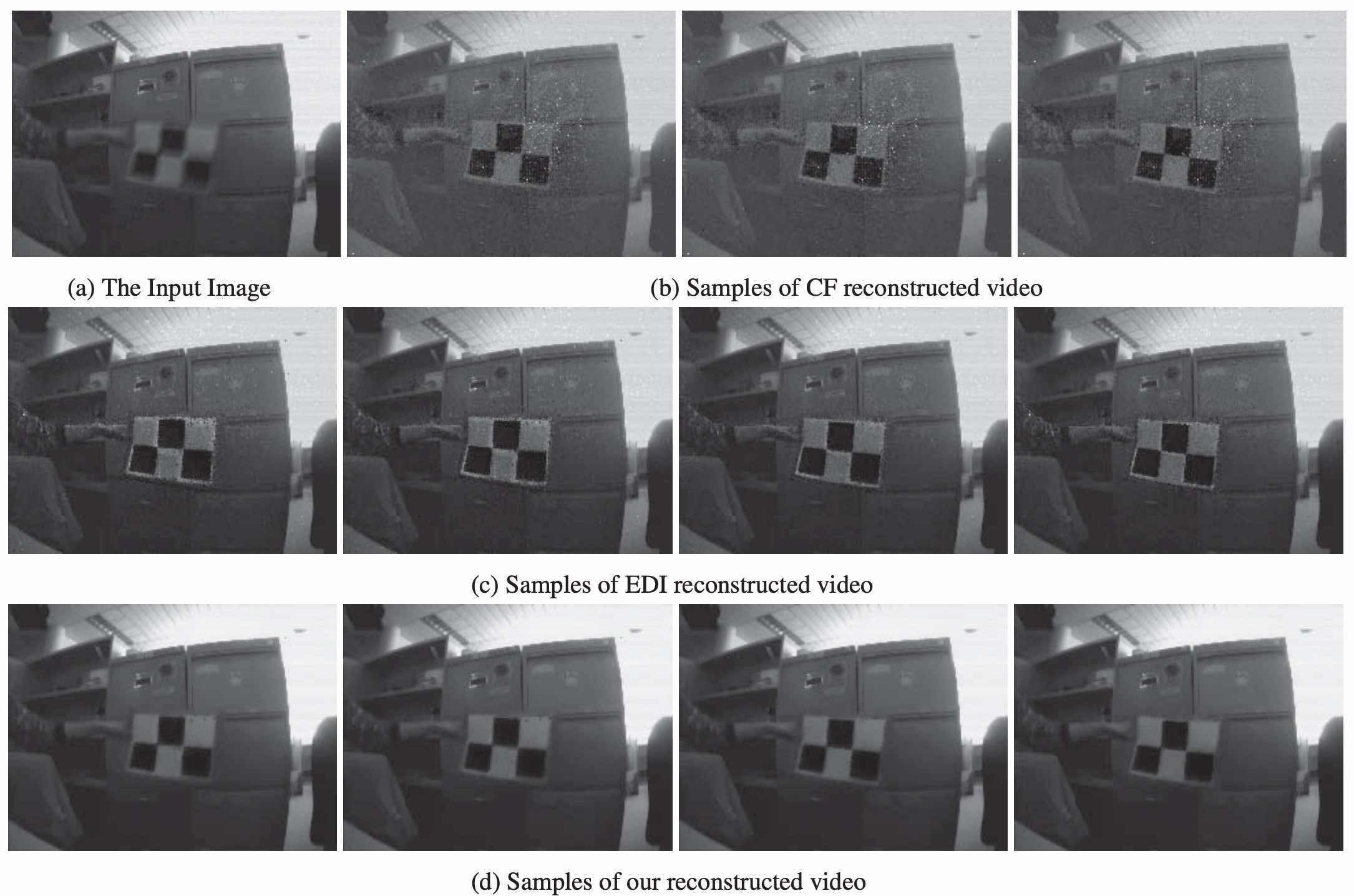 Robust Intensity Image Reconstruciton Based On Event CamerasJiang Meng, Liu Zhou, Wang Bishan, Yu Lei, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020
Robust Intensity Image Reconstruciton Based On Event CamerasJiang Meng, Liu Zhou, Wang Bishan, Yu Lei, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020@inproceedings{jiang2020robust, title = {Robust Intensity Image Reconstruciton Based On Event Cameras}, author = {Jiang, Meng and Liu, Zhou and Wang, Bishan and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen}, booktitle = {2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)}, pages = {968--972}, year = {2020} } -
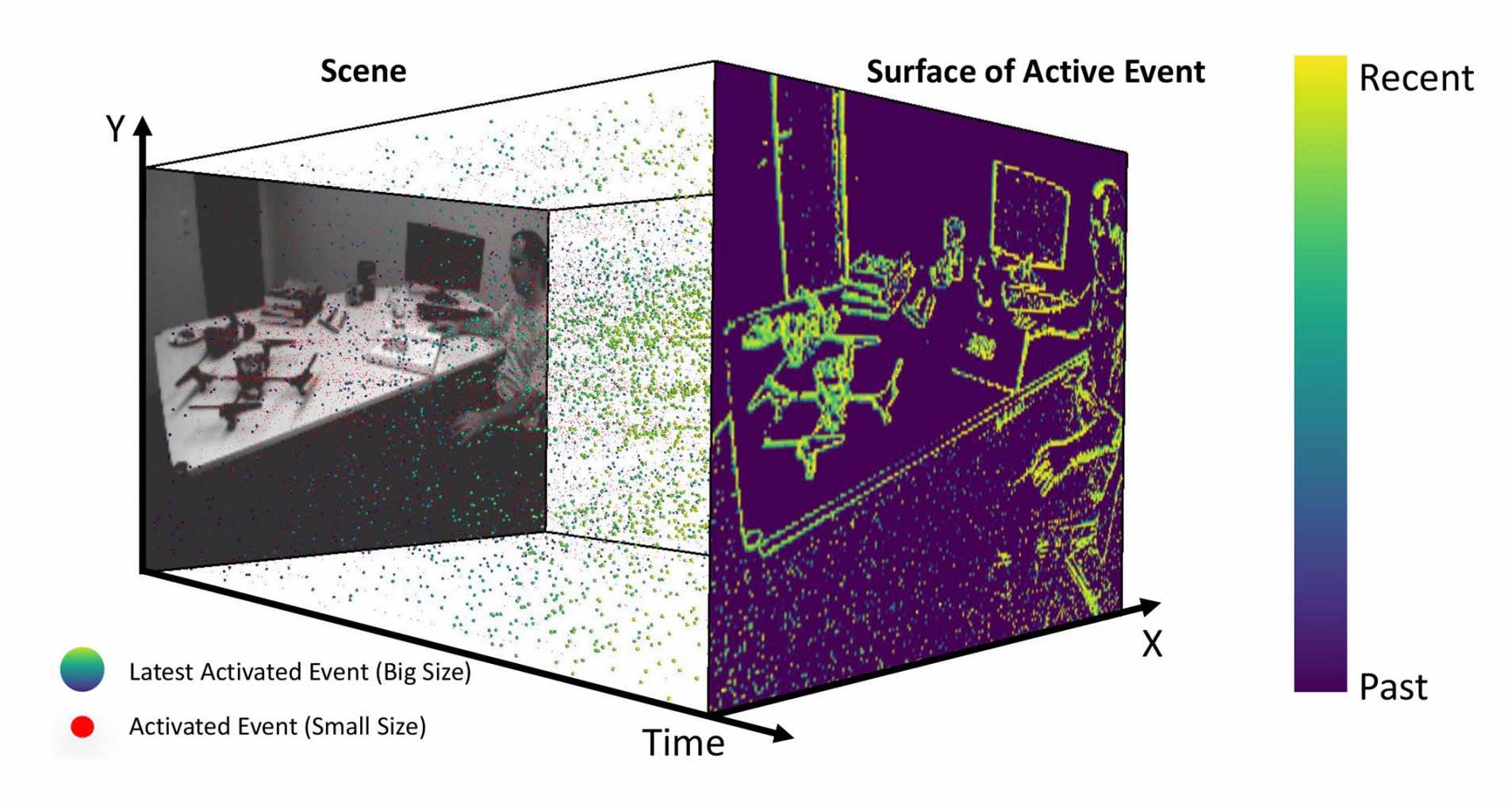 Efficient Spatial-Temporal Normalization of SAE Representation for Event CameraLin Shijie, Xu Fang, Wang Xuhong, Yang Wen, and Yu LeiIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020
Efficient Spatial-Temporal Normalization of SAE Representation for Event CameraLin Shijie, Xu Fang, Wang Xuhong, Yang Wen, and Yu LeiIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020@article{lin2020efficient, title = {Efficient Spatial-Temporal Normalization of SAE Representation for Event Camera}, author = {Lin, Shijie and Xu, Fang and Wang, Xuhong and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei}, journal = {IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters}, volume = {5}, number = {3}, pages = {4265--4272}, year = {2020} } -
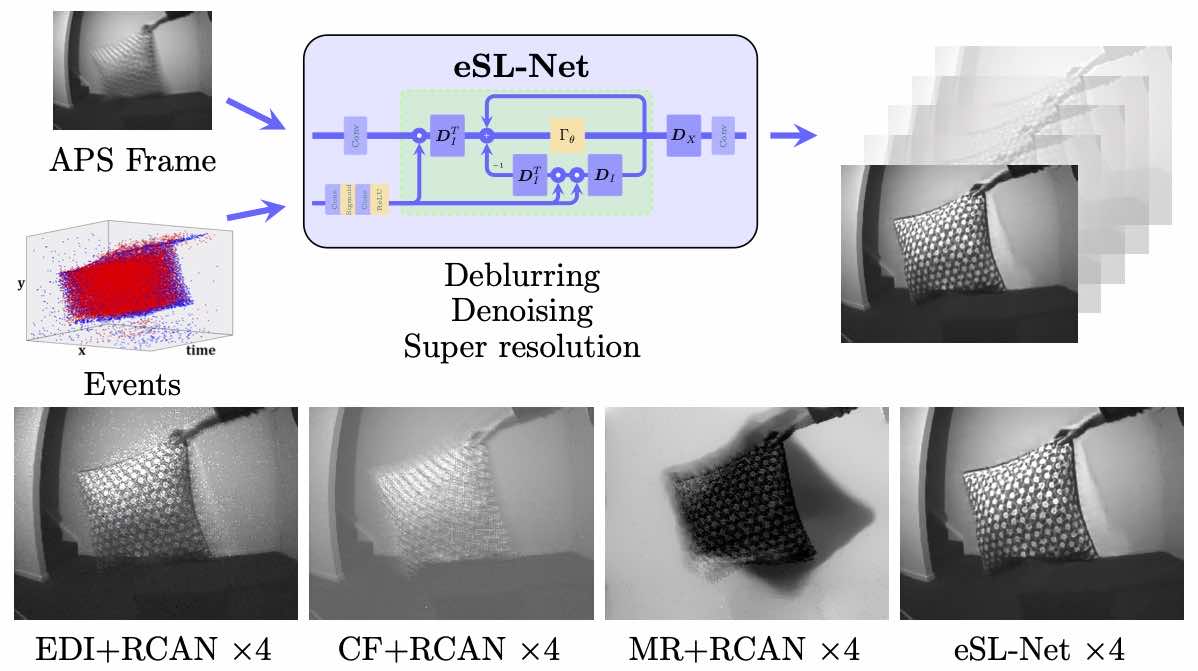 Event enhanced high-quality image recoveryWang Bishan, He Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Xia Gui-Song, and Yang WenIn ECCV, 2020🔥 An approach to super-resolve blurry images with events.
Event enhanced high-quality image recoveryWang Bishan, He Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Xia Gui-Song, and Yang WenIn ECCV, 2020🔥 An approach to super-resolve blurry images with events.@inproceedings{wang2020k, title = {Event enhanced high-quality image recovery}, booktitle = {ECCV}, author = {Wang, Bishan and He, Jingwei and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song and Yang, Wen}, year = {2020}, pages = {155--171} } -
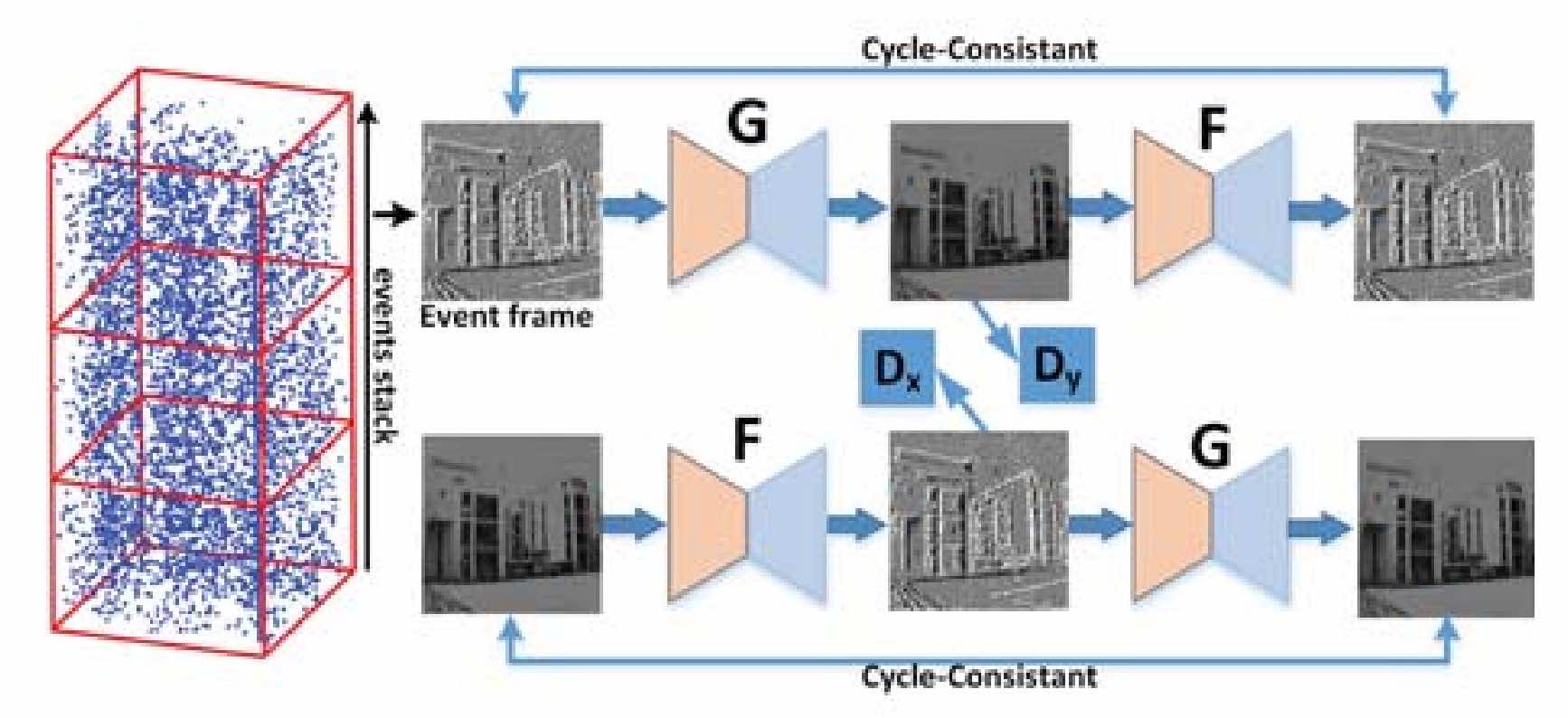 Event-based high frame-rate video reconstruction with a novel cycle-event networkSu Binyi, Yu Lei ✉️, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020
Event-based high frame-rate video reconstruction with a novel cycle-event networkSu Binyi, Yu Lei ✉️, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020@inproceedings{yu2020, title = {Event-based high frame-rate video reconstruction with a novel cycle-event network}, booktitle = {2020 {IEEE} {International} {Conference} on {Image} {Processing} ({ICIP})}, author = {Su, Binyi and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen}, year = {2020}, pages = {86--90} } -
Implicit Euler ODE networks for single-image dehazingShen Jiawei, Li Zhuoyan, Yu Lei ✉️, Xia Gui-Song, and Yang WenIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2020
@inproceedings{shen2020, title = {Implicit {Euler} {ODE} networks for single-image dehazing}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the {IEEE}/{CVF} {Conference} on {Computer} {Vision} and {Pattern} {Recognition} {Workshops}}, author = {Shen, Jiawei and Li, Zhuoyan and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song and Yang, Wen}, year = {2020}, pages = {218--219} } -
Facial Feature Embedded CycleGAN for VIS-NIR TranslationWang Huijiao, Zhang Haijian, Yu Lei, Wang Li, and Yang XuleiIn ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2020
@inproceedings{wang2020l, title = {Facial {Feature} {Embedded} {CycleGAN} for {VIS}-{NIR} {Translation}}, booktitle = {{ICASSP} 2020-2020 {IEEE} {International} {Conference} on {Acoustics}, {Speech} and {Signal} {Processing} ({ICASSP})}, author = {Wang, Huijiao and Zhang, Haijian and Yu, Lei and Wang, Li and Yang, Xulei}, year = {2020}, pages = {1903--1907} } -
Aim-Net: Bring Implicit Euler to Network DesignYuan Qiongwen, He Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, and Zheng GangIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020
@inproceedings{yuan2020, title = {Aim-{Net}: {Bring} {Implicit} {Euler} to {Network} {Design}}, booktitle = {2020 {IEEE} {International} {Conference} on {Image} {Processing} ({ICIP})}, author = {Yuan, Qiongwen and He, Jingwei and Yu, Lei and Zheng, Gang}, year = {2020}, pages = {1926--1930} } -
Structured Bayesian learning for recovery of clustered sparse signalWang Lu, Zhao Lifan, Yu Lei ✉️, Wang Jingjing, and Bi GuoanSignal Processing, 2020
This paper considers the problem of recovering sparse signals with cluster structure of unknown sizes and locations. A hybrid prior is proposed by introducing a local continuity indicator, which adaptively imposes cluster information on the sparse coefficients according to the inherent data structure. The local continuity indicator flexibly switches the prior for a sparse coefficient between a fully pattern-coupled one and an independent one, so that the estimation of the sparse coefficient can selectively use the statistical information of its neighbors. Variational Bayesian inference is used to estimate the hidden variables based on the constructed probabilistic modeling. Numerical results of comprehensive simulations and real data experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can effectively avoid the problem of structural mismatch and outperform other recently reported clustered sparse signal recovery algorithms in noisy environments.
@article{wang2020, title = {Structured {Bayesian} learning for recovery of clustered sparse signal}, volume = {166}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Wang, Lu and Zhao, Lifan and Yu, Lei and Wang, Jingjing and Bi, Guoan}, year = {2020}, pages = {107255} }
2019
-
Algorithm to compute nonlinear partial observer normal form with multiple outputsSaadi Wided, Boutat Driss, Zheng Gang, Sbita Lassaad, and Yu LeiIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019🔥 TOP Journal
It is well-known that observer design is a powerful tool to estimate the states of a dynamical system. Given a multi-output nonlinear dynamical system whose states are partially observable, this paper investigates the problem of observer design to estimate those observable states. It considers firstly a nonlinear system without inputs, and provides a set of geometric conditions, guaranteeing the existence of a change of coordinates which splits the studied nonlinear dynamical system into two subsystems, where one of them is of the well-known nonlinear observer normal form, for which a Luenberger-like observer can be designed. An extension to nonlinear systems with inputs has then been deduced.
@article{saadi2019, title = {Algorithm to compute nonlinear partial observer normal form with multiple outputs}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control}, author = {Saadi, Wided and Boutat, Driss and Zheng, Gang and Sbita, Lassaad and Yu, Lei}, year = {2019}, pages = {1--1} } -
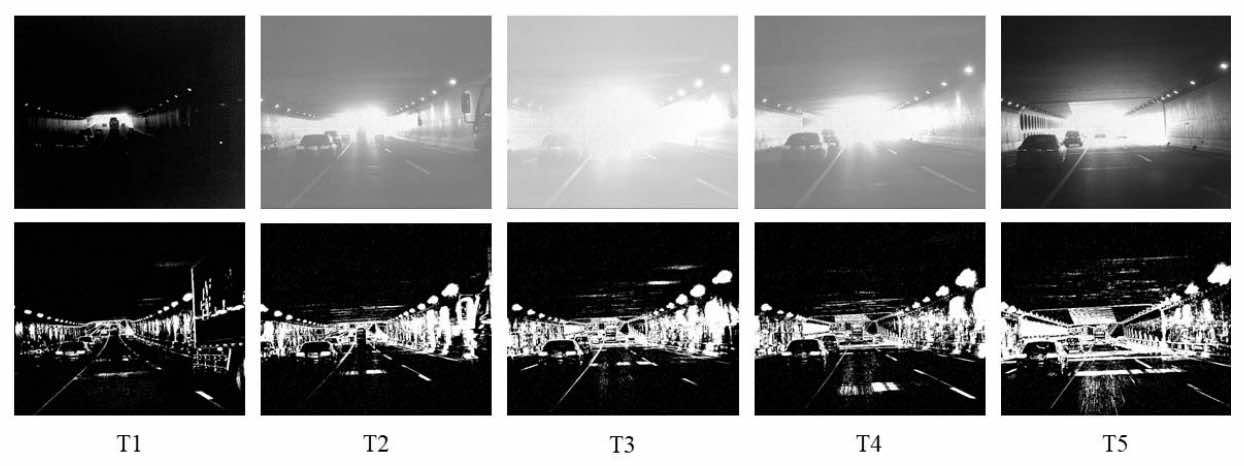 DET: A High-Resolution DVS Dataset for Lane ExtractionCheng Wensheng, Luo Hao, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019
DET: A High-Resolution DVS Dataset for Lane ExtractionCheng Wensheng, Luo Hao, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019Lane extraction is a basic yet necessary task for autonomous driving. Although past years have witnessed major advances in lane extraction with deep learning models, they all aim at ordinary RGB images generated by framebased cameras, which limits their performance in nature. To tackle this problem, we introduce Dynamic Vision Sensor (DVS), a type of event-based sensor to lane extraction task and build a high-resolution DVS dataset for lane extraction (DET). We collect the raw event data and generate 5,424 event-based sensor images with a resolution of 1280×800, the highest one among all DVS datasets available now. These images include complex traffic scenes and various lane types. All images of DET are annotated with multi-class segmentation format. The fully annotated DET images contains 17,103 lane instances, each of which is labeled pixel by pixel manually. We evaluate state-of-the-art lane extraction models on DET to build a benchmark for lane extraction task with event-based sensor images. Experimental results demonstrate that DET is quite challenging for even state-of-the-art lane extraction methods. DET is made publicly available, including the raw event data, accumulated images and labels1.
@inproceedings{cheng2019, title = {{DET}: {A} {High}-{Resolution} {DVS} {Dataset} for {Lane} {Extraction}}, booktitle = {CVPR Workshops}, author = {Cheng, Wensheng and Luo, Hao and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Chen, Shoushun and Li, Wei}, year = {2019}, pages = {10} } -
Dynamical sparse signal recovery with fixed-time convergenceRen Junying, Yu Lei ✉️, Lyu Chengcheng, Zheng Gang, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Sun HongSignal Processing, 2019
Arising in a large number of application areas, sparse recovery (SR) has been exhaustively investigated and many algorithms have been proposed. Different from the numerical methods realized by iterative algorithm, the recent continuous approach is realized through analog circuit, which takes advantage of short time-delay and fast convergence. However, the existing continuous method for SR still has the space to further improve the convergence speed. Consequently, in this paper, we propose a new dynamical continuous system to solve the sparse signal recovery problem with fixed-time convergence property.
@article{ren2019c, title = {Dynamical sparse signal recovery with fixed-time convergence}, volume = {162}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Ren, Junying and Yu, Lei and Lyu, Chengcheng and Zheng, Gang and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Sun, Hong}, year = {2019}, pages = {65--74} } -
Image Denoising via Nonlocal Low Rank Approximation With Local Structure PreservingLiu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongIEEE Access, 2019
The nuclear norm minimization method emerged from a patch-based low-rank model leads to an excellent image denoising performance, where the non-local self-similarity over image patches is exploited. However, natural images are normally with complex and irregular image patches, which cannot be well represented using only a low-rank model, and thus most of them suffer from the over-penalty problem especially for images with lots of local irregular structures (e.g., fine details or sharp edges), and then results in over-smoothing problem after denoising. On the other hand, in order to represent the irregular components, edges defined over pixel level are often exploited. While the total variation (TV) is a well-known prior to remove noises and preserve edges, it might yield undesired staircase artifacts. The total generalized variation (TGV), a generalization of TV, can largely alleviate such staircase artifacts. Consequently, in order to deal with the over-smoothing problem aroused by a low-rank model, we propose a re-weighted TGV regularized nuclear norm minimization model for local structure preserving image denoising. Thanks to the split Bregman method, our proposed model can be effectively solved. A re-weighted strategy is developed to adaptively update the weight parameters of TGV regularization. The encouraging experimental results on noisy images demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
@article{liu2019, title = {Image {Denoising} via {Nonlocal} {Low} {Rank} {Approximation} {With} {Local} {Structure} {Preserving}}, volume = {7}, journal = {IEEE Access}, author = {Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong}, year = {2019}, pages = {7117--7132} } -
A Dynamical System With Fixed Convergence Time for Sparse RecoveryRen Junying, Yu Lei ✉️, Jiang Yulun, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Sun HongIEEE Access, 2019
The sparse recovery (SR) algorithm, under the premise that signals are sparse, can be divided into two categories. One is a digital discrete method implemented via lots of iterative computations and the other is a continuous method implemented via analog circuits, which is usually faster. In this paper, we focus on the continuous method and propose a fixed-time convergence dynamical system. Compared with the existing system, it dynamically allocates the exponent according to time-varying elements of the system state, avoiding possible mismatches between the fixed exponent and some elements.
@article{ren2019, title = {A {Dynamical} {System} {With} {Fixed} {Convergence} {Time} for {Sparse} {Recovery}}, volume = {7}, journal = {IEEE Access}, author = {Ren, Junying and Yu, Lei and Jiang, Yulun and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Sun, Hong}, year = {2019}, pages = {21844--21850} } -
Block-sparsity recovery via recurrent neural networkLyu Chengcheng, Liu Zhou, and Yu Lei ✉️Signal Processing, 2019
@article{lyu2019, title = {Block-sparsity recovery via recurrent neural network}, volume = {154}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Lyu, Chengcheng and Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei}, year = {2019}, pages = {129--135} } -
 Live Demonstration: Real-Time Vi-SLAM With High-Resolution Event CameraYang Gongyu, Ye Qilin, He Wanjun, Zhou Lifeng, Chen Xinyu, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019
Live Demonstration: Real-Time Vi-SLAM With High-Resolution Event CameraYang Gongyu, Ye Qilin, He Wanjun, Zhou Lifeng, Chen Xinyu, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019Event camera is bio-inspired vision sensors that output pixel-level brightness changes asynchronously. Compared to the conventional frame-based camera, it is with high dynamic range, low latency and high sensitivity, and thus can be exploited in SLAM to tackle the problem of occasions with high-speed camera moving and low-light scenes. In this demo, we implement the visual-inerial SLAM in real time with the recently released event camera, namely, CeleX-V. With the feature of high spatial resolution (1280×800) and low latency (\textless 0.5µs), the proposed method can provide frames with abundant textures and high time response, which leads to more stable tracking ability and better performance in SLAM system.
@inproceedings{yang2019, title = {Live {Demonstration}: {Real}-{Time} {Vi}-{SLAM} {With} {High}-{Resolution} {Event} {Camera}}, booktitle = {CVPR Workshops}, author = {Yang, Gongyu and Ye, Qilin and He, Wanjun and Zhou, Lifeng and Chen, Xinyu and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Chen, Shoushun and Li, Wei}, year = {2019}, pages = {2} }
2018
-
Image restoration via Bayesian dictionary learning with nonlocal structured beta processLiu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongJournal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2018
@article{liu2018, title = {Image restoration via {Bayesian} dictionary learning with nonlocal structured beta process}, volume = {52}, journal = {Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation}, author = {Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong}, year = {2018}, pages = {159--169} } -
Image Super-Resolution via RL-CSC: When Residual Learning Meets Convolutional Sparse CodingZhang Menglei, Liu Zhou, and Yu Lei ✉️arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.11950, 2018
@article{zhang2018a, title = {Image {Super}-{Resolution} via {RL}-{CSC}: {When} {Residual} {Learning} {Meets} {Convolutional} {Sparse} {Coding}}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.11950}, author = {Zhang, Menglei and Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei}, year = {2018} }
2017
-
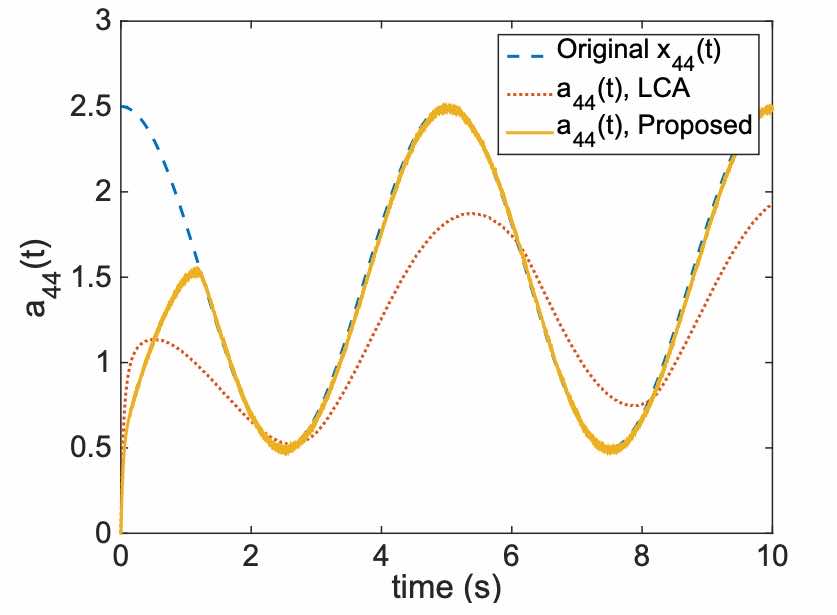 Dynamical sparse recovery with finite-time convergenceYu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean-PierreIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017🔥 TOP Journal. Recover sparse signals with analog circuits.
Dynamical sparse recovery with finite-time convergenceYu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean-PierreIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017🔥 TOP Journal. Recover sparse signals with analog circuits.@article{yu2017, title = {Dynamical sparse recovery with finite-time convergence}, volume = {65}, number = {23}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing}, author = {Yu, Lei and Zheng, Gang and Barbot, Jean-Pierre}, year = {2017}, pages = {6146--6157} } -
 Sparse Bayesian learning for image rectification with transform invariant low-rank texturesHu Shihui, Liu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongSignal Processing, 2017
Sparse Bayesian learning for image rectification with transform invariant low-rank texturesHu Shihui, Liu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongSignal Processing, 2017@article{hu2017, title = {Sparse {Bayesian} learning for image rectification with transform invariant low-rank textures}, volume = {137}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Hu, Shihui and Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong}, year = {2017}, pages = {298--308} }
2015
-
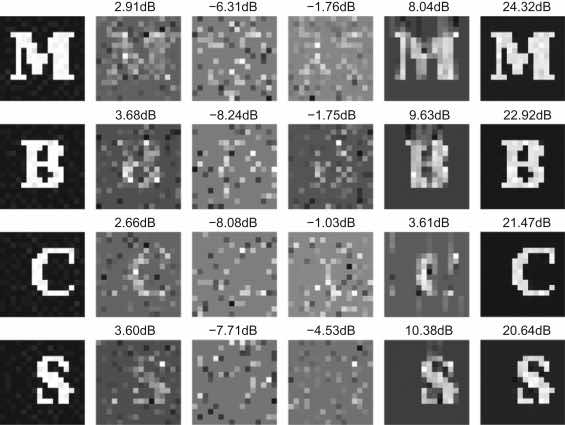 Model based Bayesian compressive sensing via local beta processYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean PierreSignal Processing, 2015
Model based Bayesian compressive sensing via local beta processYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean PierreSignal Processing, 2015@article{yu2015, title = {Model based {Bayesian} compressive sensing via local beta process}, volume = {108}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong and Zheng, Gang and Barbot, Jean Pierre}, year = {2015}, pages = {259--271} }
2012
-
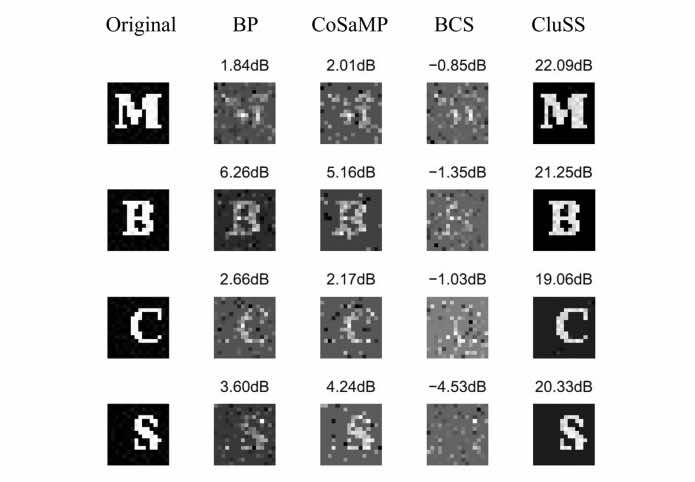 Bayesian compressive sensing for cluster structured sparse signalsYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Zheng GangSignal processing, 2012🔥 A nonparametric approach to recover cluster / block sparse signals
Bayesian compressive sensing for cluster structured sparse signalsYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Zheng GangSignal processing, 2012🔥 A nonparametric approach to recover cluster / block sparse signals@article{yu2012, title = {Bayesian compressive sensing for cluster structured sparse signals}, volume = {92}, number = {1}, journal = {Signal processing}, author = {Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Zheng, Gang}, year = {2012}, pages = {259--269} }
2010
-
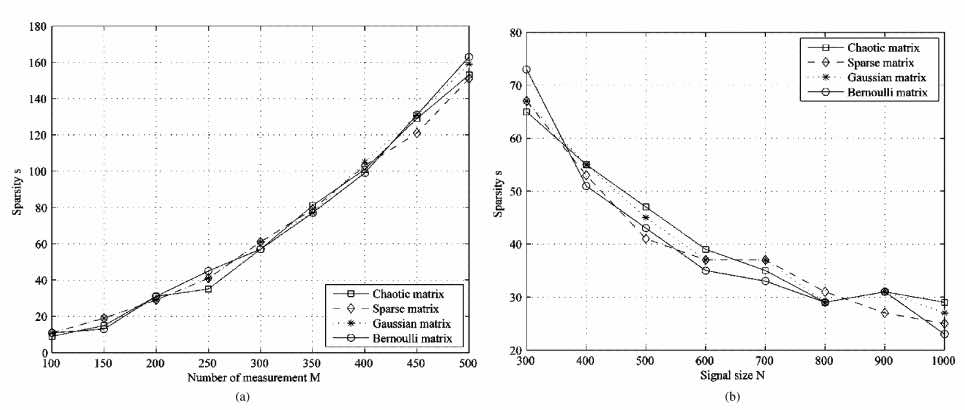 Compressive sensing with chaotic sequenceYu Lei ✉️, Barbot Jean Pierre, Zheng Gang, and Sun HongIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010🔥 A theoretical analysis of chaotic compressive sensing.
Compressive sensing with chaotic sequenceYu Lei ✉️, Barbot Jean Pierre, Zheng Gang, and Sun HongIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010🔥 A theoretical analysis of chaotic compressive sensing.@article{yu2010f, title = {Compressive sensing with chaotic sequence}, volume = {17}, number = {8}, journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters}, author = {Yu, Lei and Barbot, Jean Pierre and Zheng, Gang and Sun, Hong}, year = {2010}, pages = {731--734} } -
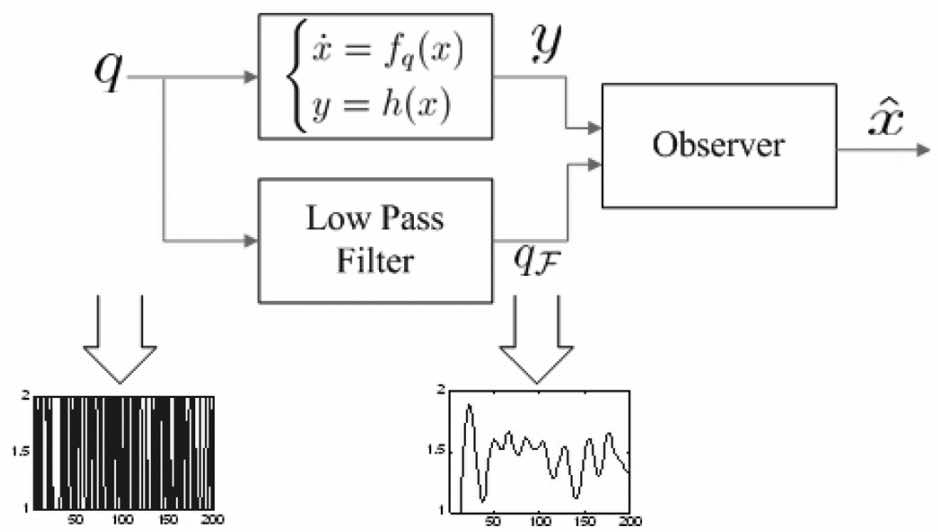 Observability forms for switched systems with zeno phenomenon or high switching frequencyYu Lei ✉️, Barbot Jean-Pierre, Boutat Driss, and Benmerzouk DjamilaIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010🔥 Top Journal
Observability forms for switched systems with zeno phenomenon or high switching frequencyYu Lei ✉️, Barbot Jean-Pierre, Boutat Driss, and Benmerzouk DjamilaIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010🔥 Top Journal@article{yu2010g, title = {Observability forms for switched systems with zeno phenomenon or high switching frequency}, volume = {56}, number = {2}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control}, author = {Yu, Lei and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Boutat, Driss and Benmerzouk, Djamila}, year = {2010}, pages = {436--441} }
Event Camera
-
 "Seeing" Electric Network Frequency From EventsXu Lexuan, Hua Guang, Zhang Haijian, Yu Lei ✉️, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2023🔥 First work on event-based ENF estimation!
"Seeing" Electric Network Frequency From EventsXu Lexuan, Hua Guang, Zhang Haijian, Yu Lei ✉️, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2023🔥 First work on event-based ENF estimation!@inproceedings{xu2023seeing, title = {"Seeing" Electric Network Frequency From Events}, author = {Xu, Lexuan and Hua, Guang and Zhang, Haijian and Yu, Lei and Qiao, Ning}, booktitle = {CVPR}, pages = {18022--18031}, year = {2023} } -
 Learning to Super-Resolve Blurry Images with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Zhang Xiang, Zhang Haijian, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia GuisongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal
Learning to Super-Resolve Blurry Images with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Zhang Xiang, Zhang Haijian, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia GuisongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal@article{yu2022b, author = {Yu, Lei and Wang, Bishan and Zhang, Xiang and Zhang, Haijian and Yang, Wen and Liu, Jianzhuang and Xia, Guisong}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}, number = {0}, title = {Learning to Super-Resolve Blurry Images with Events}, volume = {0}, year = {2023} } -
 Generalizing Event-Based Motion Deblurring in Real-World ScenariosZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia Gui-SongIn ICCV, 2023
Generalizing Event-Based Motion Deblurring in Real-World ScenariosZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Liu Jianzhuang, and Xia Gui-SongIn ICCV, 2023@inproceedings{Zhang2023, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Liu, Jianzhuang and Xia, Gui-Song}, booktitle = {ICCV}, title = {Generalizing Event-Based Motion Deblurring in Real-World Scenarios}, year = {2023} } -
 Learning to See Through with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Zhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal!
Learning to See Through with EventsYu Lei ✉️, Zhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2023🔥 Top Journal!@article{yu2022, title = {Learning to See Through with Events}, author = {Yu, Lei and Zhang, Xiang and Liao, Wei and Yang, Wen and Xia, Gui-Song}, year = {2023}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}, dataset = {https://drive.google.com/file/d/19SnoRfVgvKlUspAyzbBhtXszXkh5NsbS/view?usp=sharing} } -
 Autofocus for event camerasLin Shijie, Zhang Y, Yu Lei, Zhou B., Luo X., and Pan JianIn CVPR, 2022🔥 Oral paper
Autofocus for event camerasLin Shijie, Zhang Y, Yu Lei, Zhou B., Luo X., and Pan JianIn CVPR, 2022🔥 Oral paper@inproceedings{Lin2022, title = {Autofocus for event cameras}, author = {Lin, Shijie and Zhang, Y and Yu, Lei and Zhou, B. and Luo, X. and Pan, Jian}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2022} } -
 Synthetic aperture imaging with events and framesLiao Wei, Zhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2022🔥 A new SAI method by fusing events and frames.
Synthetic aperture imaging with events and framesLiao Wei, Zhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, and Qiao NingIn CVPR, 2022🔥 A new SAI method by fusing events and frames.@inproceedings{Liao2022, title = {Synthetic aperture imaging with events and frames}, author = {Liao, Wei and Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei and Lin, Shijie and Yang, Wen and Qiao, Ning}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2022} } -
 Unifying motion deblurring and frame interpolation with eventsZhang Xiang, and Yu Lei ✉️In CVPR, 2022🔥 Self-supervised EVDI
Unifying motion deblurring and frame interpolation with eventsZhang Xiang, and Yu Lei ✉️In CVPR, 2022🔥 Self-supervised EVDI@inproceedings{Zhang2022, title = {Unifying motion deblurring and frame interpolation with events}, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2022} } -
 Motion Deblurring with Real EventsXu Fang, Yu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Yang Wen, Xia Guisong, Jia Xu, Qiao Zhendong, and Liu JianzhuangIn ICCV, 2021🔥 A new framework to learn deblurring with real-world events
Motion Deblurring with Real EventsXu Fang, Yu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, Yang Wen, Xia Guisong, Jia Xu, Qiao Zhendong, and Liu JianzhuangIn ICCV, 2021🔥 A new framework to learn deblurring with real-world events@inproceedings{xu2021, author = {Xu, Fang and Yu, Lei and Wang, Bishan and Yang, Wen and Xia, Guisong and Jia, Xu and Qiao, Zhendong and Liu, Jianzhuang}, title = {Motion Deblurring with Real Events}, booktitle = {ICCV}, year = {2021} } -
 Event-based Synthetic Aperture Imaging with a Hybrid NetworkZhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2021🔥 Oral, Best Paper Candidate
Event-based Synthetic Aperture Imaging with a Hybrid NetworkZhang Xiang, Liao Wei, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2021🔥 Oral, Best Paper Candidate@inproceedings{zhang2021, title = {Event-based {Synthetic} {Aperture} {Imaging} with a {Hybrid} {Network}}, booktitle = {CVPR}, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Liao, Wei and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Xia, Gui-Song}, year = {2021}, pages = {14235--14244} } -
 Robust motion compensation for event cameras with smooth constraintXu Jie, Jiang Meng, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Wang WenweiIEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020
Robust motion compensation for event cameras with smooth constraintXu Jie, Jiang Meng, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, and Wang WenweiIEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020@article{xu2020a, title = {Robust motion compensation for event cameras with smooth constraint}, volume = {6}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging}, author = {Xu, Jie and Jiang, Meng and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Wang, Wenwei}, year = {2020}, pages = {604--614} } -
 Event enhanced high-quality image recoveryWang Bishan, He Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Xia Gui-Song, and Yang WenIn ECCV, 2020🔥 An approach to super-resolve blurry images with events.
Event enhanced high-quality image recoveryWang Bishan, He Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Xia Gui-Song, and Yang WenIn ECCV, 2020🔥 An approach to super-resolve blurry images with events.@inproceedings{wang2020k, title = {Event enhanced high-quality image recovery}, booktitle = {ECCV}, author = {Wang, Bishan and He, Jingwei and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song and Yang, Wen}, year = {2020}, pages = {155--171} } -
 Event-based high frame-rate video reconstruction with a novel cycle-event networkSu Binyi, Yu Lei ✉️, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020
Event-based high frame-rate video reconstruction with a novel cycle-event networkSu Binyi, Yu Lei ✉️, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020@inproceedings{yu2020, title = {Event-based high frame-rate video reconstruction with a novel cycle-event network}, booktitle = {2020 {IEEE} {International} {Conference} on {Image} {Processing} ({ICIP})}, author = {Su, Binyi and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen}, year = {2020}, pages = {86--90} } -
 Efficient Spatial-Temporal Normalization of SAE Representation for Event CameraLin Shijie, Xu Fang, Wang Xuhong, Yang Wen, and Yu LeiIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020
Efficient Spatial-Temporal Normalization of SAE Representation for Event CameraLin Shijie, Xu Fang, Wang Xuhong, Yang Wen, and Yu LeiIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020@article{lin2020efficient, title = {Efficient Spatial-Temporal Normalization of SAE Representation for Event Camera}, author = {Lin, Shijie and Xu, Fang and Wang, Xuhong and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei}, journal = {IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters}, volume = {5}, number = {3}, pages = {4265--4272}, year = {2020} } -
 Robust Intensity Image Reconstruciton Based On Event CamerasJiang Meng, Liu Zhou, Wang Bishan, Yu Lei, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020
Robust Intensity Image Reconstruciton Based On Event CamerasJiang Meng, Liu Zhou, Wang Bishan, Yu Lei, and Yang WenIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2020@inproceedings{jiang2020robust, title = {Robust Intensity Image Reconstruciton Based On Event Cameras}, author = {Jiang, Meng and Liu, Zhou and Wang, Bishan and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen}, booktitle = {2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)}, pages = {968--972}, year = {2020} } -
 Matching Neuromorphic Events and Color Images via Adversarial LearningXu Fang, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Dai Dengxin, and Xia Gui-songarXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00636, 2020
Matching Neuromorphic Events and Color Images via Adversarial LearningXu Fang, Lin Shijie, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Dai Dengxin, and Xia Gui-songarXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00636, 2020@article{xu2020matching, title = {Matching Neuromorphic Events and Color Images via Adversarial Learning}, author = {Xu, Fang and Lin, Shijie and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Dai, Dengxin and Xia, Gui-song}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00636}, year = {2020} } -
 DET: A High-Resolution DVS Dataset for Lane ExtractionCheng Wensheng, Luo Hao, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019
DET: A High-Resolution DVS Dataset for Lane ExtractionCheng Wensheng, Luo Hao, Yang Wen, Yu Lei, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019Lane extraction is a basic yet necessary task for autonomous driving. Although past years have witnessed major advances in lane extraction with deep learning models, they all aim at ordinary RGB images generated by framebased cameras, which limits their performance in nature. To tackle this problem, we introduce Dynamic Vision Sensor (DVS), a type of event-based sensor to lane extraction task and build a high-resolution DVS dataset for lane extraction (DET). We collect the raw event data and generate 5,424 event-based sensor images with a resolution of 1280×800, the highest one among all DVS datasets available now. These images include complex traffic scenes and various lane types. All images of DET are annotated with multi-class segmentation format. The fully annotated DET images contains 17,103 lane instances, each of which is labeled pixel by pixel manually. We evaluate state-of-the-art lane extraction models on DET to build a benchmark for lane extraction task with event-based sensor images. Experimental results demonstrate that DET is quite challenging for even state-of-the-art lane extraction methods. DET is made publicly available, including the raw event data, accumulated images and labels1.
@inproceedings{cheng2019, title = {{DET}: {A} {High}-{Resolution} {DVS} {Dataset} for {Lane} {Extraction}}, booktitle = {CVPR Workshops}, author = {Cheng, Wensheng and Luo, Hao and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Chen, Shoushun and Li, Wei}, year = {2019}, pages = {10} } -
 Live Demonstration: Real-Time Vi-SLAM With High-Resolution Event CameraYang Gongyu, Ye Qilin, He Wanjun, Zhou Lifeng, Chen Xinyu, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019
Live Demonstration: Real-Time Vi-SLAM With High-Resolution Event CameraYang Gongyu, Ye Qilin, He Wanjun, Zhou Lifeng, Chen Xinyu, Yu Lei ✉️, Yang Wen, Chen Shoushun, and Li WeiIn CVPR Workshops, 2019Event camera is bio-inspired vision sensors that output pixel-level brightness changes asynchronously. Compared to the conventional frame-based camera, it is with high dynamic range, low latency and high sensitivity, and thus can be exploited in SLAM to tackle the problem of occasions with high-speed camera moving and low-light scenes. In this demo, we implement the visual-inerial SLAM in real time with the recently released event camera, namely, CeleX-V. With the feature of high spatial resolution (1280×800) and low latency (\textless 0.5µs), the proposed method can provide frames with abundant textures and high time response, which leads to more stable tracking ability and better performance in SLAM system.
@inproceedings{yang2019, title = {Live {Demonstration}: {Real}-{Time} {Vi}-{SLAM} {With} {High}-{Resolution} {Event} {Camera}}, booktitle = {CVPR Workshops}, author = {Yang, Gongyu and Ye, Qilin and He, Wanjun and Zhou, Lifeng and Chen, Xinyu and Yu, Lei and Yang, Wen and Chen, Shoushun and Li, Wei}, year = {2019}, pages = {2} }
Sparse Recovery
-
 Spiking Sparse Recovery with Non-convex PenaltiesZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Eldar YoninaIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023
Spiking Sparse Recovery with Non-convex PenaltiesZhang Xiang, Yu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Eldar YoninaIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023@article{yu2022a, title = {Spiking Sparse Recovery with Non-convex Penalties}, author = {Zhang, Xiang and Yu, Lei and Zheng, Gang and Eldar, Yonina}, year = {2023}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing} } -
Structured Bayesian learning for recovery of clustered sparse signalWang Lu, Zhao Lifan, Yu Lei ✉️, Wang Jingjing, and Bi GuoanSignal Processing, 2020
This paper considers the problem of recovering sparse signals with cluster structure of unknown sizes and locations. A hybrid prior is proposed by introducing a local continuity indicator, which adaptively imposes cluster information on the sparse coefficients according to the inherent data structure. The local continuity indicator flexibly switches the prior for a sparse coefficient between a fully pattern-coupled one and an independent one, so that the estimation of the sparse coefficient can selectively use the statistical information of its neighbors. Variational Bayesian inference is used to estimate the hidden variables based on the constructed probabilistic modeling. Numerical results of comprehensive simulations and real data experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can effectively avoid the problem of structural mismatch and outperform other recently reported clustered sparse signal recovery algorithms in noisy environments.
@article{wang2020, title = {Structured {Bayesian} learning for recovery of clustered sparse signal}, volume = {166}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Wang, Lu and Zhao, Lifan and Yu, Lei and Wang, Jingjing and Bi, Guoan}, year = {2020}, pages = {107255} } -
 Distributed compressive sensing via LSTM-Aided sparse Bayesian learningZhang Haijian, Zhang Wusheng, Yu Lei ✉️, and Bi GuoanSignal Processing, 2020
Distributed compressive sensing via LSTM-Aided sparse Bayesian learningZhang Haijian, Zhang Wusheng, Yu Lei ✉️, and Bi GuoanSignal Processing, 2020@article{zhang2020f, title = {Distributed compressive sensing via {LSTM}-{Aided} sparse {Bayesian} learning}, volume = {176}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Zhang, Haijian and Zhang, Wusheng and Yu, Lei and Bi, Guoan}, year = {2020}, pages = {107656} } -
Block-sparsity recovery via recurrent neural networkLyu Chengcheng, Liu Zhou, and Yu Lei ✉️Signal Processing, 2019
@article{lyu2019, title = {Block-sparsity recovery via recurrent neural network}, volume = {154}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Lyu, Chengcheng and Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei}, year = {2019}, pages = {129--135} } -
Dynamical sparse signal recovery with fixed-time convergenceRen Junying, Yu Lei ✉️, Lyu Chengcheng, Zheng Gang, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Sun HongSignal Processing, 2019
Arising in a large number of application areas, sparse recovery (SR) has been exhaustively investigated and many algorithms have been proposed. Different from the numerical methods realized by iterative algorithm, the recent continuous approach is realized through analog circuit, which takes advantage of short time-delay and fast convergence. However, the existing continuous method for SR still has the space to further improve the convergence speed. Consequently, in this paper, we propose a new dynamical continuous system to solve the sparse signal recovery problem with fixed-time convergence property.
@article{ren2019c, title = {Dynamical sparse signal recovery with fixed-time convergence}, volume = {162}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Ren, Junying and Yu, Lei and Lyu, Chengcheng and Zheng, Gang and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Sun, Hong}, year = {2019}, pages = {65--74} } -
A Dynamical System With Fixed Convergence Time for Sparse RecoveryRen Junying, Yu Lei ✉️, Jiang Yulun, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Sun HongIEEE Access, 2019
The sparse recovery (SR) algorithm, under the premise that signals are sparse, can be divided into two categories. One is a digital discrete method implemented via lots of iterative computations and the other is a continuous method implemented via analog circuits, which is usually faster. In this paper, we focus on the continuous method and propose a fixed-time convergence dynamical system. Compared with the existing system, it dynamically allocates the exponent according to time-varying elements of the system state, avoiding possible mismatches between the fixed exponent and some elements.
@article{ren2019, title = {A {Dynamical} {System} {With} {Fixed} {Convergence} {Time} for {Sparse} {Recovery}}, volume = {7}, journal = {IEEE Access}, author = {Ren, Junying and Yu, Lei and Jiang, Yulun and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Sun, Hong}, year = {2019}, pages = {21844--21850} } -
Image Super-Resolution via RL-CSC: When Residual Learning Meets Convolutional Sparse CodingZhang Menglei, Liu Zhou, and Yu Lei ✉️arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.11950, 2018
@article{zhang2018a, title = {Image {Super}-{Resolution} via {RL}-{CSC}: {When} {Residual} {Learning} {Meets} {Convolutional} {Sparse} {Coding}}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.11950}, author = {Zhang, Menglei and Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei}, year = {2018} } -
 Sparse Bayesian learning for image rectification with transform invariant low-rank texturesHu Shihui, Liu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongSignal Processing, 2017
Sparse Bayesian learning for image rectification with transform invariant low-rank texturesHu Shihui, Liu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongSignal Processing, 2017@article{hu2017, title = {Sparse {Bayesian} learning for image rectification with transform invariant low-rank textures}, volume = {137}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Hu, Shihui and Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong}, year = {2017}, pages = {298--308} } -
 Dynamical sparse recovery with finite-time convergenceYu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean-PierreIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017🔥 TOP Journal. Recover sparse signals with analog circuits.
Dynamical sparse recovery with finite-time convergenceYu Lei ✉️, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean-PierreIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017🔥 TOP Journal. Recover sparse signals with analog circuits.@article{yu2017, title = {Dynamical sparse recovery with finite-time convergence}, volume = {65}, number = {23}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing}, author = {Yu, Lei and Zheng, Gang and Barbot, Jean-Pierre}, year = {2017}, pages = {6146--6157} } -
 Model based Bayesian compressive sensing via local beta processYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean PierreSignal Processing, 2015
Model based Bayesian compressive sensing via local beta processYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Zheng Gang, and Barbot Jean PierreSignal Processing, 2015@article{yu2015, title = {Model based {Bayesian} compressive sensing via local beta process}, volume = {108}, journal = {Signal Processing}, author = {Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong and Zheng, Gang and Barbot, Jean Pierre}, year = {2015}, pages = {259--271} } -
 Bayesian compressive sensing for cluster structured sparse signalsYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Zheng GangSignal processing, 2012🔥 A nonparametric approach to recover cluster / block sparse signals
Bayesian compressive sensing for cluster structured sparse signalsYu Lei ✉️, Sun Hong, Barbot Jean-Pierre, and Zheng GangSignal processing, 2012🔥 A nonparametric approach to recover cluster / block sparse signals@article{yu2012, title = {Bayesian compressive sensing for cluster structured sparse signals}, volume = {92}, number = {1}, journal = {Signal processing}, author = {Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Zheng, Gang}, year = {2012}, pages = {259--269} }
Image Processing
-
 Image super-resolution by learning weighted convolutional sparse codingHe Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Liu Zhou, and Yang WenSignal, Image and Video Processing, 2021
Image super-resolution by learning weighted convolutional sparse codingHe Jingwei, Yu Lei ✉️, Liu Zhou, and Yang WenSignal, Image and Video Processing, 2021@article{he2021, title = {Image super-resolution by learning weighted convolutional sparse coding}, journal = {Signal, Image and Video Processing}, author = {He, Jingwei and Yu, Lei and Liu, Zhou and Yang, Wen}, year = {2021}, pages = {1--9} } -
Image Denoising via Nonlocal Low Rank Approximation With Local Structure PreservingLiu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongIEEE Access, 2019
The nuclear norm minimization method emerged from a patch-based low-rank model leads to an excellent image denoising performance, where the non-local self-similarity over image patches is exploited. However, natural images are normally with complex and irregular image patches, which cannot be well represented using only a low-rank model, and thus most of them suffer from the over-penalty problem especially for images with lots of local irregular structures (e.g., fine details or sharp edges), and then results in over-smoothing problem after denoising. On the other hand, in order to represent the irregular components, edges defined over pixel level are often exploited. While the total variation (TV) is a well-known prior to remove noises and preserve edges, it might yield undesired staircase artifacts. The total generalized variation (TGV), a generalization of TV, can largely alleviate such staircase artifacts. Consequently, in order to deal with the over-smoothing problem aroused by a low-rank model, we propose a re-weighted TGV regularized nuclear norm minimization model for local structure preserving image denoising. Thanks to the split Bregman method, our proposed model can be effectively solved. A re-weighted strategy is developed to adaptively update the weight parameters of TGV regularization. The encouraging experimental results on noisy images demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
@article{liu2019, title = {Image {Denoising} via {Nonlocal} {Low} {Rank} {Approximation} {With} {Local} {Structure} {Preserving}}, volume = {7}, journal = {IEEE Access}, author = {Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong}, year = {2019}, pages = {7117--7132} } -
Image restoration via Bayesian dictionary learning with nonlocal structured beta processLiu Zhou, Yu Lei ✉️, and Sun HongJournal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2018
@article{liu2018, title = {Image restoration via {Bayesian} dictionary learning with nonlocal structured beta process}, volume = {52}, journal = {Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation}, author = {Liu, Zhou and Yu, Lei and Sun, Hong}, year = {2018}, pages = {159--169} }
Others
-
 Dynamic Coarse-To-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Ding Jian, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei ✉️, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2023
Dynamic Coarse-To-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Ding Jian, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei ✉️, and Xia Gui-SongIn CVPR, 2023@inproceedings{Xu_2023_CVPR, author = {Xu, Chang and Ding, Jian and Wang, Jinwang and Yang, Wen and Yu, Huai and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song}, title = {Dynamic Coarse-To-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object Detection}, booktitle = {CVPR}, year = {2023}, pages = {7318-7328} } -
 Learning to Extract Building Footprints from Off-Nadir Aerial ImagesWang Jinwang, Meng L., Li W., Yang Wen, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2022🔥 Top Journal
Learning to Extract Building Footprints from Off-Nadir Aerial ImagesWang Jinwang, Meng L., Li W., Yang Wen, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2022🔥 Top Journal@article{wang2022, title = {Learning to Extract Building Footprints from Off-Nadir Aerial Images}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}, author = {Wang, Jinwang and Meng, L. and Li, W. and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song}, year = {2022} } -
 RFLA: Gaussian Receptive Field Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIn European Conference on Computer Vision, 2022
RFLA: Gaussian Receptive Field Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object DetectionXu Chang, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Huai, Yu Lei, and Xia Gui-SongIn European Conference on Computer Vision, 2022@inproceedings{xu2022rfla, title = {RFLA: Gaussian Receptive Field Based Label Assignment for Tiny Object Detection}, author = {Xu, Chang and Wang, Jinwang and Yang, Wen and Yu, Huai and Yu, Lei and Xia, Gui-Song}, booktitle = {European Conference on Computer Vision}, pages = {526--543}, year = {2022}, organization = {Springer} } -
 Single Image Deraining With Continuous Rain Density EstimationYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, He Jingwei, Xia Guisong, and Yang WenIEEE Transaction on Multimedia, 2021🔥 A new deraining method considering rain densities.
Single Image Deraining With Continuous Rain Density EstimationYu Lei ✉️, Wang Bishan, He Jingwei, Xia Guisong, and Yang WenIEEE Transaction on Multimedia, 2021🔥 A new deraining method considering rain densities.@article{key, author = {Yu, Lei and Wang, Bishan and He, Jingwei and Xia, Guisong and Yang, Wen}, journal = {IEEE Transaction on Multimedia}, number = {0}, title = {Single Image Deraining With Continuous Rain Density Estimation}, volume = {0}, year = {2021} } -
 ULSD: Unified line segment detection across pinhole, fisheye, and spherical camerasLi Hao, Yu Huai, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Lei ✉️, and Scherer SebastianISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021🔥 Best Paper of 2021 in ISPRS
ULSD: Unified line segment detection across pinhole, fisheye, and spherical camerasLi Hao, Yu Huai, Wang Jinwang, Yang Wen, Yu Lei ✉️, and Scherer SebastianISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021🔥 Best Paper of 2021 in ISPRS@article{li2021, title = {{ULSD}: {Unified} line segment detection across pinhole, fisheye, and spherical cameras}, volume = {178}, journal = {ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing}, author = {Li, Hao and Yu, Huai and Wang, Jinwang and Yang, Wen and Yu, Lei and Scherer, Sebastian}, year = {2021}, pages = {187--202} } -
Algorithm to compute nonlinear partial observer normal form with multiple outputsSaadi Wided, Boutat Driss, Zheng Gang, Sbita Lassaad, and Yu LeiIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019🔥 TOP Journal
It is well-known that observer design is a powerful tool to estimate the states of a dynamical system. Given a multi-output nonlinear dynamical system whose states are partially observable, this paper investigates the problem of observer design to estimate those observable states. It considers firstly a nonlinear system without inputs, and provides a set of geometric conditions, guaranteeing the existence of a change of coordinates which splits the studied nonlinear dynamical system into two subsystems, where one of them is of the well-known nonlinear observer normal form, for which a Luenberger-like observer can be designed. An extension to nonlinear systems with inputs has then been deduced.
@article{saadi2019, title = {Algorithm to compute nonlinear partial observer normal form with multiple outputs}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control}, author = {Saadi, Wided and Boutat, Driss and Zheng, Gang and Sbita, Lassaad and Yu, Lei}, year = {2019}, pages = {1--1} } -
 Observability forms for switched systems with zeno phenomenon or high switching frequencyYu Lei ✉️, Barbot Jean-Pierre, Boutat Driss, and Benmerzouk DjamilaIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010🔥 Top Journal
Observability forms for switched systems with zeno phenomenon or high switching frequencyYu Lei ✉️, Barbot Jean-Pierre, Boutat Driss, and Benmerzouk DjamilaIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010🔥 Top Journal@article{yu2010g, title = {Observability forms for switched systems with zeno phenomenon or high switching frequency}, volume = {56}, number = {2}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control}, author = {Yu, Lei and Barbot, Jean-Pierre and Boutat, Driss and Benmerzouk, Djamila}, year = {2010}, pages = {436--441} }